Which micronutrients are frequently linked to supporting healthy testosterone levels in men?

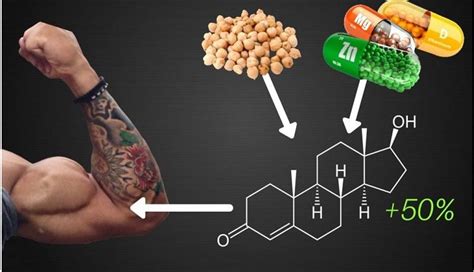
Testosterone is a vital hormone in men, playing a crucial role in maintaining muscle mass, bone density, red blood cell production, fat distribution, libido, and overall mood. While factors like age, lifestyle, and genetics heavily influence testosterone levels, a growing body of research points to the profound impact of specific micronutrients. A deficiency in these essential vitamins and minerals can potentially hinder the body’s ability to produce and utilize testosterone effectively.
The Micronutrient Connection to Male Hormonal Health
Understanding the intricate relationship between nutrition and hormone regulation is key to optimizing men’s health. Micronutrients act as cofactors, enzymes, and signaling molecules in numerous biochemical reactions, including those involved in steroid hormone synthesis. When these essential elements are scarce, the entire system can be thrown off balance.

1. Vitamin D (The Sunshine Vitamin)
Often referred to as a prohormone, Vitamin D is perhaps one of the most widely studied micronutrients regarding its impact on testosterone. Receptors for Vitamin D are found in the testes, and studies have shown a correlation between sufficient Vitamin D levels and higher total and free testosterone. It’s believed to play a role in testicular function and the regulation of the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen. Adequate sunlight exposure is the primary way to obtain Vitamin D, but dietary sources like fatty fish, fortified foods, and supplements are also important, especially in regions with limited sun.
2. Zinc (The Essential Mineral)
Zinc is another critical mineral for male reproductive health. It’s involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including protein synthesis and cellular metabolism. For testosterone, zinc is known to affect the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland, which in turn stimulates testosterone production in the testes. Additionally, zinc acts as an aromatase inhibitor, helping to prevent the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. Shellfish (especially oysters), red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and whole grains are excellent sources of zinc.

3. Magnesium (The Muscle and Nerve Regulator)
Magnesium is essential for hundreds of bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, blood pressure regulation, and bone health. Research suggests that magnesium can improve free testosterone levels by reducing its binding to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). When testosterone is bound to SHBG, it’s less biologically active. Therefore, higher magnesium intake can potentially make more free testosterone available to the body. Leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and dark chocolate are rich in magnesium.
4. Boron (The Trace Element)
Although a trace element, boron has garnered attention for its potential role in hormone regulation. Studies have indicated that boron supplementation may significantly increase free testosterone levels while decreasing estrogen. It’s thought to do this by reducing SHBG and inhibiting aromatase activity. Boron is found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes.
Other Supporting Micronutrients
- Vitamin K2: Emerging research suggests Vitamin K2 might play a role in testicular health and testosterone production, potentially by activating certain enzymes.
- Selenium: An important antioxidant, selenium contributes to overall reproductive health and may indirectly support testosterone by protecting testicular cells from oxidative damage.
- B Vitamins: Especially B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are crucial for energy metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis, which can indirectly support hormonal balance and overall well-being.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach
While specific micronutrients are undoubtedly important, it’s crucial to remember that healthy testosterone levels are a result of a holistic approach to health. A balanced diet rich in whole foods, regular exercise (especially strength training), adequate sleep, stress management, and maintaining a healthy body weight all contribute significantly. Supplementation should always be considered in consultation with a healthcare professional, as excessive intake of certain micronutrients can be harmful. Blood tests can accurately identify deficiencies, guiding personalized dietary and supplementation strategies.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy testosterone levels is multifaceted, with nutrition playing a foundational role. Vitamin D, Zinc, Magnesium, and Boron stand out as key micronutrients frequently linked to directly and indirectly supporting testosterone production and utilization in men. Ensuring adequate intake of these essential elements through a nutrient-dense diet, and potentially through targeted supplementation under professional guidance, can be a vital component of optimizing male hormonal health and overall vitality. Prioritizing a balanced lifestyle that encompasses proper nutrition, physical activity, and stress management is the most effective strategy for long-term well-being.









