Which foods boost natural testosterone for men’s performance?

Understanding Testosterone and Its Importance
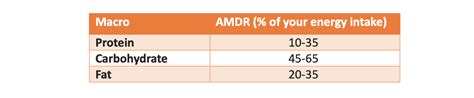
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in various aspects of men’s health, including muscle mass, bone density, libido, mood, and energy levels. While synthetic supplements exist, many men prefer a natural approach to optimizing their hormone levels. Diet is a powerful tool in this endeavor, providing essential nutrients that support the body’s natural testosterone production. Incorporating specific foods can be a safe and effective way to enhance men’s performance and overall well-being.
Zinc: A Critical Mineral for Testosterone Synthesis
Zinc is an indispensable mineral directly involved in testosterone production. Studies have shown that even a marginal zinc deficiency can lead to a significant drop in testosterone levels. Ensuring adequate intake of zinc-rich foods is therefore paramount.
- Oysters: Often hailed as an aphrodisiac, oysters are one of the richest natural sources of zinc.
- Red Meat: Lean cuts of beef and lamb provide substantial amounts of zinc, alongside other important nutrients like iron and protein.
- Pumpkin Seeds: A fantastic plant-based source, pumpkin seeds are also rich in magnesium and antioxidants.
- Beans and Legumes: Chickpeas, lentils, and black beans offer good amounts of zinc, particularly for those on a vegetarian diet.

Vitamin D: The Sunshine Hormone’s Connection
Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D is actually a hormone precursor that plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including testosterone regulation. Research indicates a strong correlation between healthy Vitamin D levels and higher testosterone.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and tuna are excellent sources of Vitamin D.
- Fortified Dairy and Plant Milks: Many milk products and plant-based alternatives are fortified with Vitamin D.
- Egg Yolks: While in smaller amounts, egg yolks do contribute to Vitamin D intake.
Healthy Fats: Essential for Hormone Production
Contrary to outdated beliefs, healthy fats are crucial for hormone synthesis, including testosterone. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats provide the necessary building blocks for steroid hormones.
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats and Vitamin B6, avocados support hormone balance.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds offer healthy fats, fiber, and other beneficial nutrients.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil, a staple of the Mediterranean diet, is packed with monounsaturated fats and antioxidants.
Magnesium: A Key Mineral for Free Testosterone
Magnesium is another mineral that plays a significant role in testosterone levels. It helps reduce oxidative stress and can increase free testosterone, which is the biologically active form of the hormone. Many men are deficient in this essential mineral.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are magnesium powerhouses.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread provide magnesium and fiber.
- Dark Chocolate: A delicious source of magnesium (and antioxidants) in moderation.

Cruciferous Vegetables: Balancing Estrogen for Testosterone
While not directly boosting testosterone, cruciferous vegetables contain compounds like Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C) that help metabolize and excrete excess estrogen. A better estrogen-to-testosterone ratio can indirectly support higher testosterone levels.
- Broccoli: A versatile and nutrient-dense vegetable.
- Cauliflower: Another excellent source of I3C.
- Brussels Sprouts: Packed with vitamins, minerals, and estrogen-balancing compounds.

Incorporating a wide variety of these nutrient-dense foods into your daily diet can significantly contribute to supporting natural testosterone production and improving men’s performance. Remember that a holistic approach, including regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management, is also vital for optimal hormonal health. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes or starting new supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions.