What’s the most efficient workout split for maximum male strength & growth?

When it comes to building a powerful physique and maximizing muscle gains, the way you organize your training — your workout split — is just as crucial as the effort you put into each rep. A well-designed split can optimize recovery, volume, and frequency, all critical components for continuous progress in strength and hypertrophy.
Understanding Workout Splits and Their Importance
A workout split defines how you divide your training sessions throughout the week, determining which muscle groups you work on particular days. The goal is to stimulate muscle protein synthesis, allow for adequate recovery, and progressively overload your muscles without overtraining. For men specifically targeting maximum strength and growth, the choice of split can significantly impact results.

Key Principles for Maximum Strength and Growth
Regardless of the split you choose, several universal principles must be applied for optimal results:
- Progressive Overload: Continuously challenge your muscles by increasing weight, reps, sets, or decreasing rest times.
- Volume: The total amount of work performed (sets x reps x weight). Adequate volume is necessary for hypertrophy.
- Frequency: How often you train a muscle group. Higher frequency can lead to more opportunities for muscle protein synthesis.
- Intensity: How close to failure you train and the load used. High intensity is vital for strength gains.
- Recovery: Essential for muscle repair and growth, encompassing sleep, nutrition, and rest days.
Popular Workout Splits for Maximizing Gains
Full Body Workout Split
In a full body split, you train all major muscle groups in each session, typically 3 times a week. This allows for high frequency for each muscle group, which can be beneficial for strength and hypertrophy, especially for beginners and intermediates. It also offers good recovery time between sessions.
Pros:
- High frequency for muscle groups (3x per week).
- Excellent for beginners to learn movements and build foundational strength.
- Efficient use of time; missing a session doesn’t leave a muscle group untrained for long.
Cons:
- Lower per-session volume for individual muscle groups.
- Can be very demanding if training with high intensity.

Upper/Lower Split
This split divides your body into upper and lower body workouts, often performed 4 days a week (e.g., Upper, Lower, Rest, Upper, Lower, Rest, Rest). Each muscle group is trained twice a week, striking a good balance between frequency and per-session volume.
Pros:
- Good frequency (2x per week per muscle group).
- Allows for higher volume per session for specific muscle groups compared to full body.
- Balanced approach suitable for intermediates and advanced lifters.
Cons:
- Requires 4 training days, which might be a time commitment.
Push/Pull/Legs (PPL) Split
The PPL split divides your training into three categories: Push (chest, shoulders, triceps), Pull (back, biceps), and Legs (quads, hamstrings, glutes, calves). This split is commonly run 6 days a week (Push, Pull, Legs, Push, Pull, Legs, Rest), meaning each muscle group is trained twice a week.
Pros:
- Excellent frequency (2x per week per muscle group).
- Allows for high volume per session for related muscle groups.
- Logical organization, grouping muscles with similar functions.
- Very popular and effective for hypertrophy and strength.
Cons:
- Requires 6 training days, demanding significant time commitment and discipline.
- Recovery can be an issue if volume and intensity are too high for some individuals.
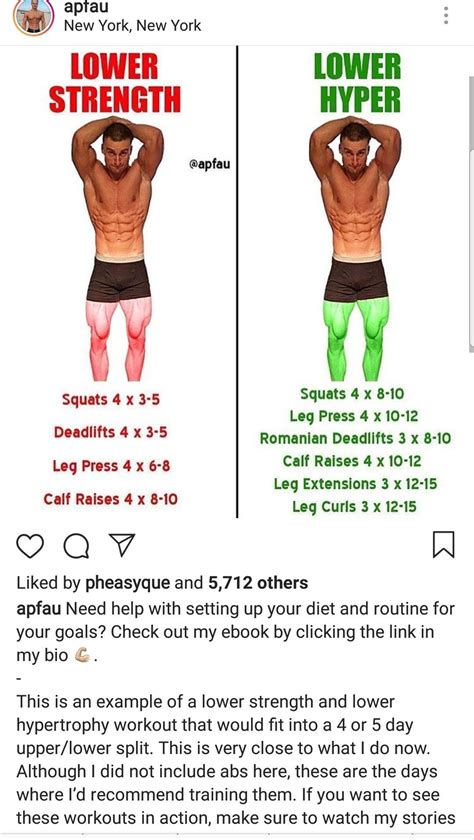
Bro Split (Body Part Split)
The traditional “bro split” dedicates each training session to one or two muscle groups (e.g., Monday: Chest, Tuesday: Back, Wednesday: Legs, etc.), typically training each group once a week. While popular among bodybuilders, its efficiency for overall strength and growth is often debated.
Pros:
- Allows for very high per-session volume for a single muscle group.
- Plenty of recovery time (7 days) for each muscle group between sessions.
Cons:
- Low frequency (1x per week per muscle group) is generally less optimal for muscle protein synthesis and strength progression compared to higher frequency splits.
- More prone to overtraining a single muscle group if volume is excessive.

Choosing Your Optimal Split: Factors to Consider
The ‘most efficient’ split isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. It depends on several individual factors:
- Training Experience: Beginners often thrive on full body or upper/lower due to higher frequency and less per-session fatigue. Advanced lifters might benefit from PPL or even more specialized 5-day splits to manage higher volume and intensity.
- Time Availability: If you can only train 3 days a week, a full body split is ideal. If you have 4-6 days, Upper/Lower or PPL become viable and highly effective.
- Recovery Capacity: Adequate sleep, nutrition, and stress management play a huge role. More frequent, intense training requires superior recovery.
- Specific Goals: While this article focuses on strength and growth, specific goals (e.g., powerlifting, endurance) might slightly alter the optimal approach.

The Verdict: Which Split is Most Efficient?
For maximizing male strength and growth, workout splits that allow for a muscle group to be trained with sufficient volume 2-3 times per week tend to be the most efficient. This higher frequency maximizes muscle protein synthesis over time and provides more opportunities for progressive overload.
- For most individuals, particularly intermediates: The Upper/Lower split (4 days/week) and the Push/Pull/Legs (PPL) split (6 days/week) stand out as highly effective options. They offer a fantastic balance of frequency and volume, allowing for significant gains in both strength and size.
- For beginners: A Full Body split (3 days/week) is excellent for building a strong foundation and mastering movement patterns.
- For advanced lifters: PPL or more customized 4-5 day splits (e.g., Upper, Lower, Rest, Push, Pull, Legs) can be incredibly effective, provided recovery is meticulously managed.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the most efficient workout split is one you can adhere to consistently, that allows for progressive overload, and supports adequate recovery. Experiment with different splits, listen to your body, and continually adjust your training based on your progress and recovery. Focus on the core principles of training, and pair your chosen split with smart nutrition and ample rest, and you’ll be well on your way to maximizing your strength and muscle growth.







