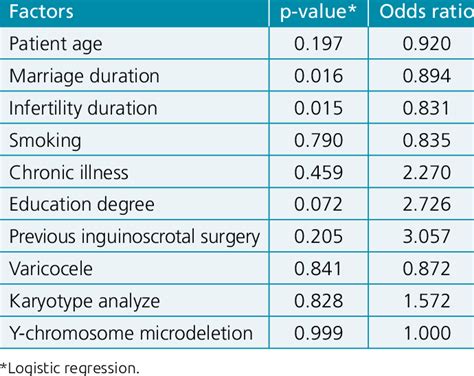
What specific trace mineral is critical for sperm quality and testosterone synthesis in men?
Zinc: The Indispensable Trace Mineral for Male Reproductive Health
In the intricate landscape of male reproductive health, various nutrients play pivotal roles, but one specific trace mineral consistently emerges as critically important for both sperm quality and testosterone synthesis: zinc. Often overlooked in general dietary discussions, zinc’s impact on male fertility and hormonal balance is profound and multifaceted, making it an essential element for men’s overall well-being.
The Cornerstone of Sperm Quality
Zinc is integral to numerous cellular processes, and its presence in high concentrations in seminal fluid underscores its importance for sperm health. It contributes significantly to sperm production (spermatogenesis), maturation, and motility. Adequate zinc levels help maintain the structural integrity of sperm, protecting them from oxidative damage, which can impair their ability to reach and fertilize an egg. Studies have consistently linked sufficient zinc intake to improved sperm count, morphology (shape), and progressive motility, all crucial factors for male fertility.

Fueling Testosterone Synthesis
Beyond its direct influence on sperm, zinc is a vital cofactor in the enzymatic reactions involved in testosterone synthesis. It plays a role in regulating the Leydig cells in the testes, which are responsible for producing testosterone. Research indicates that zinc deficiency can lead to decreased testosterone levels, potentially contributing to symptoms like reduced libido, fatigue, and impaired muscle mass. By ensuring proper enzyme function and hormone regulation, zinc directly supports the body’s ability to produce and maintain healthy testosterone levels, which are fundamental for virility and overall male health.

The Risks of Deficiency
Given its critical roles, a deficiency in zinc can have significant repercussions for male reproductive health. Mild to moderate zinc deficiency is not uncommon, especially in individuals with restrictive diets, certain medical conditions, or those consuming diets high in phytates (found in legumes and whole grains), which can inhibit zinc absorption. Symptoms of deficiency can include impaired immune function, hair loss, poor wound healing, and, most notably, reduced sperm quality, lower testosterone levels, and decreased libido. These issues can collectively impact fertility and overall quality of life.
Optimizing Zinc Intake: Dietary Sources and Considerations
Fortunately, zinc is readily available in a variety of foods. Excellent dietary sources include oysters (which are exceptionally high in zinc), red meat, poultry, beans, nuts (like cashews and almonds), whole grains, and dairy products. For individuals concerned about their zinc intake, especially those with dietary restrictions or diagnosed deficiencies, supplementation under medical guidance may be considered. However, it’s crucial to avoid excessive intake, as very high doses of zinc can interfere with the absorption of other essential minerals, such as copper.

Conclusion: A Small Mineral with a Massive Impact
In summary, zinc stands as the unequivocal trace mineral critical for sperm quality and testosterone synthesis in men. Its indispensable roles in spermatogenesis, sperm protection, and hormonal regulation underscore its profound impact on male fertility and overall endocrine health. Prioritizing adequate zinc intake through a balanced diet is a fundamental step toward supporting robust reproductive function and maintaining optimal masculine vitality. For men aiming to optimize their fertility and hormonal balance, understanding and addressing their zinc status is paramount.










