What specific carotenoid, abundant in cooked tomatoes, is often highlighted for its potential role in supporting men’s prostate health?

Lycopene: The Star Carotenoid for Prostate Health
When discussing the specific carotenoid abundant in cooked tomatoes and its potential role in supporting men’s prostate health, the answer is resoundingly lycopene. This vibrant red pigment, responsible for the characteristic color of tomatoes, watermelon, and pink grapefruit, is a powerful antioxidant that has garnered significant attention in nutritional science.
Unlike some nutrients that are diminished by cooking, lycopene’s bioavailability actually increases when tomatoes are cooked and processed. Heat breaks down the plant cell walls, releasing the lycopene and making it more accessible for absorption by the body. This is why tomato paste, sauces, and cooked tomato products are often considered superior sources of lycopene compared to raw tomatoes.

How Lycopene Supports Prostate Health
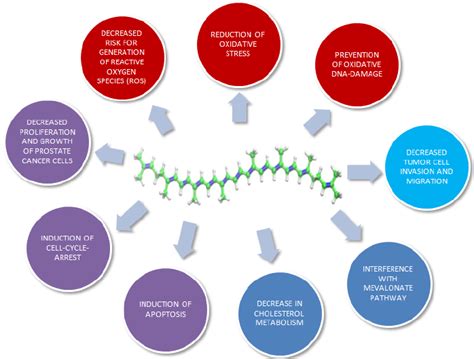
The potential health benefits of lycopene for the prostate stem primarily from its potent antioxidant properties. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, is believed to contribute to various chronic diseases, including prostate issues. Lycopene helps neutralize these harmful free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative damage to cells and DNA.
Beyond its antioxidant role, research suggests that lycopene may also possess anti-inflammatory properties and could influence cellular signaling pathways. Some studies indicate that lycopene may help inhibit the proliferation of certain cancer cells and promote apoptosis (programmed cell death) in prostate cancer cells, though more extensive human trials are needed to confirm these mechanisms conclusively. Epidemiological studies have frequently observed a correlation between higher dietary lycopene intake and a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
Maximizing Lycopene Intake for Optimal Benefit
To maximize the absorption of lycopene, it’s recommended to consume cooked tomato products with a small amount of healthy fat. Lycopene is fat-soluble, meaning it’s better absorbed when ingested with fats, such as olive oil, avocado, or nuts. So, enjoying a pasta sauce with olive oil or a tomato soup with a drizzle of healthy fat can significantly enhance its uptake.
While cooked tomatoes are a primary source, other foods like watermelon, pink grapefruit, guava, and papaya also contain lycopene. Incorporating a variety of these red and pink fruits into your diet can contribute to a robust lycopene intake.

A Holistic Approach to Men’s Health
While lycopene from cooked tomatoes offers significant potential benefits for prostate health, it’s crucial to remember that it’s one component of a broader, holistic approach to well-being. A diet rich in various fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, coupled with regular physical activity and a healthy lifestyle, provides the most comprehensive support for overall health, including prostate health.
Men concerned about their prostate health should consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice, regular screenings, and comprehensive care. Nutritional strategies, including adequate lycopene intake, should complement, not replace, medical guidance.

Conclusion
Lycopene stands out as the specific carotenoid in cooked tomatoes frequently lauded for its potential positive impact on men’s prostate health. Its powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, enhanced absorption from cooked sources, make it a valuable addition to a health-conscious diet. By embracing foods rich in lycopene and adopting a balanced lifestyle, men can take proactive steps toward supporting their prostate and overall health.









