What nutritional strategies boost men’s testosterone & vitality naturally?

Understanding Testosterone and Men’s Vitality
Testosterone is a pivotal hormone for men, influencing everything from muscle mass and bone density to mood, energy levels, and sexual health. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, often leading to symptoms such as fatigue, reduced libido, decreased muscle mass, and mood disturbances. While various factors contribute to this decline, nutrition plays an incredibly powerful role in supporting and optimizing natural testosterone production and overall vitality. By focusing on specific foods and dietary patterns, men can significantly impact their hormonal health and quality of life.
Essential Nutrients for Testosterone Production
Certain vitamins and minerals are non-negotiable when it comes to healthy testosterone levels. Deficiencies in these micronutrients can directly impair hormone synthesis.
- Zinc: This mineral is crucial for testosterone production and helps prevent its conversion to estrogen. Foods rich in zinc include oysters, red meat, shellfish, beans, nuts, and whole grains.
- Vitamin D: Often called the ‘sunshine vitamin,’ Vitamin D functions as a steroid hormone in the body and is strongly linked to testosterone levels. Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy products, and direct sunlight exposure are primary sources.
- Magnesium: Involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, magnesium is vital for muscle function, energy production, and, importantly, free testosterone levels. Leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains are excellent sources.
- Selenium: An important antioxidant, selenium supports thyroid function, which in turn influences hormone balance. Brazil nuts, seafood, and organ meats are good sources.

The Power of Healthy Fats
Forget the old advice to shun all fats; healthy fats are fundamental building blocks for hormone production, including testosterone. The body uses cholesterol, derived from dietary fats, to synthesize steroid hormones.
- Monounsaturated Fats: Found in avocados, olive oil, and nuts (almonds, pecans), these fats have been shown to support testosterone levels.
- Polyunsaturated Fats (Omega-3s): Present in fatty fish (salmon, tuna), flaxseeds, and walnuts, Omega-3s reduce inflammation, which can indirectly help optimize hormone function.
It’s crucial to distinguish between healthy fats and trans fats or excessive saturated fats, which can negatively impact cardiovascular health and hormone balance. Focus on whole, unprocessed sources.
Quality Protein and Complex Carbohydrates
Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily function, all of which are linked to healthy testosterone. Aim for adequate protein intake from lean sources.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, fish, eggs, and legumes provide the amino acids necessary for muscle maintenance and recovery, indirectly supporting hormonal health.
Carbohydrates, particularly complex ones, provide the energy needed for workouts and daily functions, preventing the body from entering a catabolic state that can suppress testosterone. They also help manage cortisol levels, a stress hormone that can counteract testosterone.
- Complex Carbs: Whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa), sweet potatoes, and root vegetables provide sustained energy and fiber.
- Fiber: Crucial for gut health and regulating blood sugar, fiber helps to excrete excess estrogen, allowing testosterone to have a more prominent role.

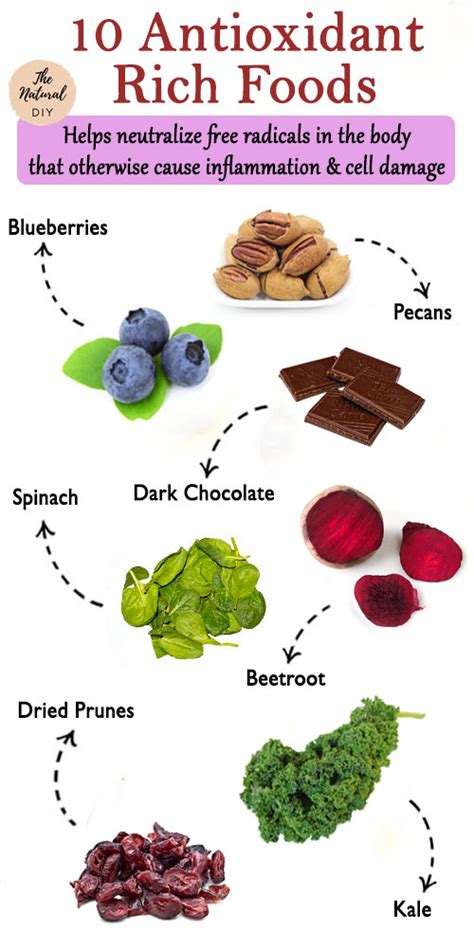
Antioxidant-Rich Foods and Limiting Harmful Substances
Oxidative stress and inflammation can damage cells and negatively impact hormone production. Incorporating a wide variety of antioxidant-rich foods can combat this.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, and colorful peppers are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that protect cells.
Equally important are the foods and substances to limit or avoid:
- Processed Foods and Sugars: High intake of refined sugars and ultra-processed foods can lead to insulin resistance, inflammation, and weight gain, all detrimental to testosterone levels.
- Excessive Alcohol: Chronic or heavy alcohol consumption can directly impair testosterone synthesis and increase its conversion to estrogen.
- Phytoestrogens: While some are beneficial, excessive consumption of certain soy products might have estrogenic effects for some individuals, though research is mixed and individual responses vary.
Hydration and Gut Health
Don’t underestimate the power of proper hydration. Water is vital for every bodily function, including hormone transport and nutrient absorption. Furthermore, a healthy gut microbiome plays a role in overall health and can influence hormone metabolism. Consuming fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, along with a high-fiber diet, can support gut health.
Boosting testosterone and vitality naturally through nutrition isn’t about quick fixes but about cultivating sustainable eating habits. It involves a holistic approach that prioritizes whole, unprocessed foods rich in essential nutrients, healthy fats, quality proteins, and complex carbohydrates, while limiting inflammatory and hormone-disrupting substances. Combining these nutritional strategies with adequate sleep, regular exercise, and stress management will provide the most comprehensive support for men looking to optimize their hormonal health and overall well-being naturally.










