What nutrition strategies boost male testosterone & vitality?

Maintaining optimal testosterone levels and overall vitality is crucial for men’s health, impacting everything from energy levels and mood to muscle mass and libido. While various factors influence these aspects, nutrition stands out as a foundational pillar. By strategically adjusting dietary intake, men can naturally support hormone production and enhance their well-being.
The Foundational Role of Macronutrients
A balanced intake of macronutrients—fats, proteins, and carbohydrates—is essential for testosterone synthesis and overall energy.
Healthy Fats: Non-Negotiable for Hormone Production
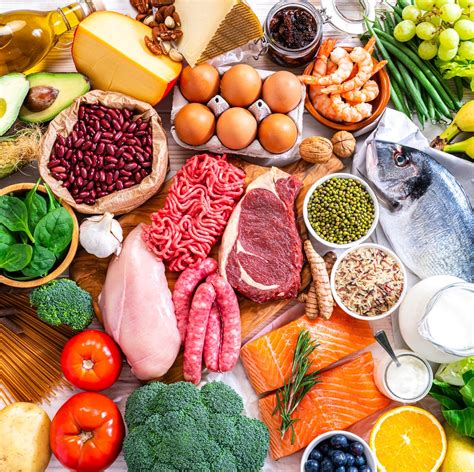
Contrary to old beliefs, healthy fats are vital for testosterone production. Cholesterol, derived from dietary fats, is a precursor to testosterone. Focus on monounsaturated fats found in avocados, olive oil, and nuts, and polyunsaturated fats from fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel) and seeds (chia, flax). Avoid trans fats and excessive saturated fats from processed foods, which can negatively impact cardiovascular health and hormone balance.

Adequate Protein: Building Blocks and Satiety
Sufficient protein intake is crucial for muscle maintenance and growth, which indirectly supports testosterone levels, especially when combined with resistance training. Aim for lean protein sources such as grass-fed beef, poultry, eggs, fish, and plant-based options like legumes and tofu. Protein also helps with satiety and stable blood sugar, preventing energy crashes that can affect vitality.
Complex Carbohydrates: Fuel for Energy and Recovery
While low-carb diets have gained popularity, adequate complex carbohydrates are important for energy, recovery, and preventing undue stress on the body, which can suppress testosterone. Choose whole grains like oats, quinoa, brown rice, as well as starchy vegetables (sweet potatoes, squash), and a wide variety of non-starchy vegetables. These provide sustained energy and fiber, supporting gut health.
Key Micronutrients for Testosterone & Vitality
Specific vitamins and minerals act as cofactors in testosterone synthesis and play crucial roles in overall male vitality.
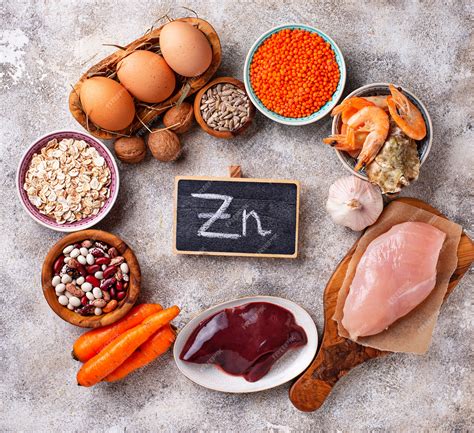
Zinc: A Powerful Mineral
Zinc is directly involved in testosterone production. Deficiencies are linked to lower levels. Excellent sources include oysters, red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and pumpkin seeds.

Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
Often referred to as a pro-hormone, Vitamin D plays a significant role in male hormone health. While sunlight exposure is the primary source, dietary options include fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and certain mushrooms. Supplementation might be necessary for many, especially during winter months.
Magnesium: Muscle and Hormone Support
Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including those related to testosterone and muscle function. Rich sources include leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds, legumes, and dark chocolate.
Selenium & B Vitamins: Essential Cofactors
Selenium, found in Brazil nuts, seafood, and organ meats, is important for thyroid function and reproductive health. Various B vitamins, especially B6 and B12, contribute to energy metabolism and nervous system function, indirectly supporting vitality and stress management.
Foods to Emphasize and Avoid
Prioritize Whole, Unprocessed Foods
The cornerstone of a testosterone-boosting diet is whole, unprocessed foods. This means plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Antioxidant-rich foods like berries, dark leafy greens, and colorful vegetables help combat oxidative stress, which can negatively impact hormone health.

Cruciferous Vegetables for Estrogen Balance
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage contain compounds (like Indole-3-Carbinol) that help the body metabolize estrogen more efficiently, which can be beneficial for maintaining a healthy testosterone-to-estrogen balance.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
To optimize testosterone and vitality, it’s crucial to reduce or eliminate:
- Excessive Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates: These can lead to insulin resistance, inflammation, and weight gain, all detrimental to hormone balance.
- Trans Fats and Processed Foods: Often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium, these offer little nutritional value and can promote inflammation.
- Excessive Alcohol: Chronic heavy alcohol consumption can directly impair testosterone production and liver function.

Beyond the Plate: The Lifestyle Connection
While nutrition is paramount, it works synergistically with other lifestyle factors. Adequate sleep, regular physical activity (especially strength training), and effective stress management are all critical for optimizing testosterone and overall vitality. Nutrition supports these factors by providing the necessary fuel and building blocks for a resilient body and mind.
Conclusion
Boosting male testosterone and vitality through nutrition is not about quick fixes but about adopting a sustainable, whole-food-focused diet. By emphasizing healthy fats, lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and key micronutrients like zinc and Vitamin D, and by limiting processed foods and excessive sugar, men can lay a strong foundation for optimal hormonal health and an energetic, vibrant life. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice tailored to individual needs.