What key diet changes boost male energy and natural testosterone for peak performance?

Fueling Male Vitality: The Dietary Roadmap to Enhanced Energy and Testosterone
For men seeking to optimize their physical and mental prowess, diet plays an indispensable role. Beyond just managing weight, strategic nutritional choices can directly influence energy levels, hormonal balance, and overall vitality, especially natural testosterone production. This vital hormone is crucial for muscle mass, bone density, mood, and libido. Understanding which dietary shifts can positively impact these areas is the first step towards achieving peak performance.
The journey to enhanced energy and optimized testosterone begins with recognizing the profound connection between what you eat and how your body functions at a foundational level. It’s about more than just calories; it’s about nutrient density and the specific compounds that act as catalysts for these crucial bodily processes.

Essential Micronutrients: The Building Blocks of Testosterone
Certain vitamins and minerals are non-negotiable for healthy testosterone synthesis and energy metabolism. Ensuring adequate intake of these can significantly move the needle:
- Zinc: This mineral is critical for testosterone production and immune function. Deficiencies are linked to lower T levels. Incorporate zinc-rich foods like oysters, red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and whole grains.
- Vitamin D: Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D is actually a pro-hormone with a strong correlation to testosterone levels. Aim for sun exposure when possible, and include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy, and egg yolks in your diet.
- Magnesium: Involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, magnesium supports muscle function, energy production, and, importantly, free testosterone levels. Leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains are excellent sources.
The Power of Healthy Fats and Quality Protein
Don’t shy away from fats; the right kind is crucial for hormone health. Cholesterol, a precursor to testosterone, is derived from dietary fats. Furthermore, adequate protein intake is fundamental for muscle repair, growth, and sustained energy.
- Healthy Fats: Focus on monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Avocados, olive oil, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia, flax), and fatty fish (rich in Omega-3s) should be staples. These fats not only support hormone production but also reduce inflammation.
- Lean Proteins: Include a variety of high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, eggs, fish, and plant-based options like lentils and beans. Protein helps maintain muscle mass, which is directly linked to higher testosterone levels, and provides sustained energy.

Strategic Carbohydrate Intake for Sustained Energy
While often demonized, carbohydrates are vital for energy, especially for physically active men. The key lies in choosing complex, unrefined carbohydrates that provide a steady release of glucose, preventing energy crashes and supporting overall bodily functions.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Opt for whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa), sweet potatoes, and root vegetables. These provide fiber, essential nutrients, and stable energy levels without the sudden insulin spikes associated with simple sugars.
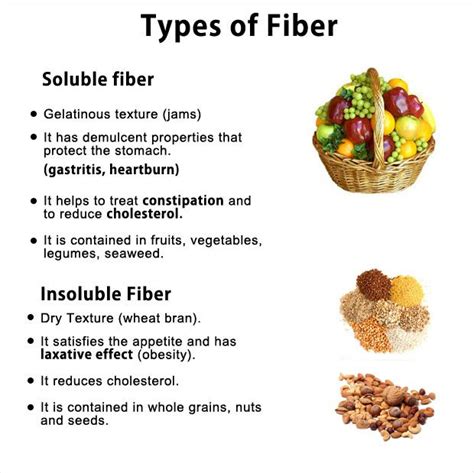
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Beyond carbohydrates, fiber found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps regulate blood sugar, promotes gut health, and assists in hormone metabolism.
Foods to Embrace and Foods to Limit for Optimal Hormonal Balance
Beyond specific nutrients, certain food categories have a direct impact on male hormone health.
Foods to Embrace:
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage contain compounds (like indole-3-carbinol) that help the body metabolize estrogen, potentially leading to a better testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
- Garlic: Contains allicin, which may help lower cortisol (a stress hormone that can suppress testosterone) and improve blood flow.
- Berries: Rich in antioxidants, berries help combat oxidative stress, which can negatively impact hormone health.
- Eggs: A complete protein source, eggs also provide healthy fats, Vitamin D, and selenium, all beneficial for testosterone.

Foods to Limit or Avoid:
- Processed Foods and Added Sugars: These contribute to inflammation, insulin resistance, and weight gain, all of which can negatively impact testosterone and energy.
- Excessive Alcohol: Chronic heavy drinking can damage testicular cells and disrupt hormone pathways.
- Trans Fats and Unhealthy Saturated Fats: Found in fried foods and many processed snacks, these can harm cardiovascular health and hormone production.
Hydration and Lifestyle Synergy
While diet is paramount, its effects are amplified when combined with other healthy lifestyle choices. Adequate hydration is crucial for every bodily function, including hormone transport and energy metabolism. Aim for plenty of water throughout the day. Furthermore, regular exercise (especially strength training), sufficient sleep, and stress management are powerful allies in boosting natural testosterone and overall energy. A holistic approach that integrates mindful eating with these lifestyle factors creates the most robust foundation for peak male performance.

Conclusion
Optimizing male energy and natural testosterone production isn’t about quick fixes but rather a sustained commitment to intelligent dietary choices. By prioritizing essential micronutrients, healthy fats, quality proteins, and complex carbohydrates, while limiting detrimental processed foods, men can unlock a profound sense of vitality, enhance their physical capabilities, and foster mental clarity. These dietary shifts are not merely about performance; they are about cultivating long-term health and well-being, paving the way for a more energized and robust life.









