What diet strategy best reduces belly fat safely?

Understanding the Challenge of Belly Fat
Belly fat, particularly visceral fat that surrounds organs, is more than just a cosmetic concern; it’s a significant indicator of increased risk for chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. Safely and effectively targeting this stubborn fat requires a strategic, sustainable dietary approach, rather than quick fixes or extreme deprivation. This article explores the most effective and safe diet strategies to help you reduce belly fat and improve your overall health.
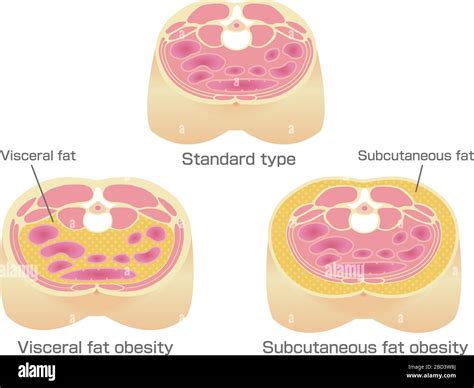
The Core Principles of Belly Fat Reduction
While spot reduction is a myth, a well-structured diet can significantly impact abdominal fat stores. The foundation lies in creating a moderate calorie deficit, meaning you consume slightly fewer calories than you burn, prompting your body to tap into fat reserves. However, the quality of those calories is just as crucial as the quantity.
Prioritize Protein and Fiber
Protein is a powerhouse for fat loss. It increases satiety, reduces cravings, and has a higher thermic effect, meaning your body burns more calories digesting it. Aim for a good source of lean protein at every meal (chicken, fish, legumes, tofu, eggs). Soluble fiber, found in oats, beans, fruits, and vegetables, is particularly effective. It absorbs water, forming a gel that slows food passage, promoting fullness and reducing the absorption of calories from food. Studies show a direct link between increased soluble fiber intake and reduced visceral fat.
Key Dietary Strategies for a Flatter Midsection
1. The Mediterranean Diet: A Holistic Approach
Often lauded for its heart-health benefits, the Mediterranean diet is also excellent for reducing belly fat. It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods: plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and healthy fats like olive oil. Lean protein sources, primarily fish and poultry, are consumed in moderation, while red meat is limited. This eating pattern naturally reduces intake of refined carbohydrates and added sugars, two major culprits behind belly fat accumulation, while promoting nutrient density and satiety.

2. Thoughtful Low-Carb Approaches
Reducing carbohydrate intake, especially refined carbs and sugary drinks, can be highly effective. When you consume excessive simple carbohydrates, your body quickly converts them to glucose, leading to insulin spikes. High insulin levels promote fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area. Opt for complex carbohydrates from whole grains, vegetables, and fruits in controlled portions, and prioritize lean protein and healthy fats. This doesn’t necessarily mean a strict ketogenic diet, but rather a mindful reduction in overall carb load, focusing on quality sources.
3. Incorporating Healthy Fats
Don’t fear fats, but choose them wisely. Healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil) are vital for hormone production and satiety. They can help reduce inflammation, which is often linked to increased visceral fat. However, remember that all fats are calorie-dense, so portion control is key.

4. Mindful Eating and Portion Control
Regardless of the specific diet strategy, mindful eating is paramount. Paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring your meals can prevent overeating and improve digestion. Portion control, especially with calorie-dense foods, ensures you maintain that crucial calorie deficit without feeling deprived.
Beyond Diet: Complementary Strategies
While diet is the primary driver for belly fat reduction, it’s not the only factor. Regular physical activity, particularly a combination of strength training and cardio, can enhance fat loss and muscle preservation. Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga is also vital, as high cortisol levels (the stress hormone) can contribute to abdominal fat storage. Adequate sleep, typically 7-9 hours per night, supports metabolic health and can help regulate appetite hormones.

Safety First: Important Considerations
Before embarking on any significant dietary change, it’s always wise to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized advice, especially if you have underlying health conditions. Focus on gradual, sustainable changes rather than drastic measures that are difficult to maintain and can lead to nutrient deficiencies or rebound weight gain. The goal is long-term health, not just a temporary aesthetic change.

Conclusion
Safely reducing belly fat is an achievable goal that hinges on consistent, informed dietary choices. Strategies that prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, ample protein and fiber, healthy fats, and controlled portions—such as the Mediterranean diet or a thoughtful low-carb approach—are highly effective. Coupled with regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep, these dietary strategies can lead to not only a smaller waistline but also profound improvements in overall health and well-being.









