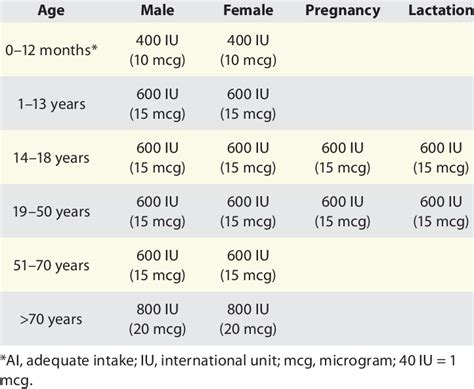
What is the recommended daily intake of Vitamin D for an average adult?
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin D for most average adults is 600 International Units (IU) or 15 micrograms (mcg), vital for bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.





