
How to break workout plateaus for peak strength gains and sustained progress?
Breaking through workout plateaus is essential for continued strength gains and sustained progress, requiring strategic adjustments to training, nutrition, and recovery.

Breaking through workout plateaus is essential for continued strength gains and sustained progress, requiring strategic adjustments to training, nutrition, and recovery.

Effective post-workout recovery is crucial for optimizing muscle repair, restoring energy, and achieving sustained gains in both strength and overall athletic performance.

Discover how a high-intensity training protocol can dramatically reduce gym time while maximizing strength and muscle gains through strategic, focused effort.
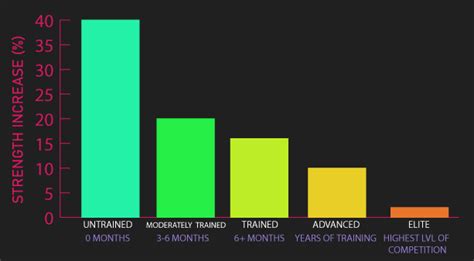
Understanding how often to train specific muscle groups is crucial for maximizing both strength development and muscle growth, requiring a balance between stimulus and recovery.

Effectively optimizing post-workout recovery is paramount for accelerating strength gains, enhancing muscle repair, and consistently achieving peak physical performance.

Busy men can unlock consistent muscle gains and peak performance by strategically optimizing their recovery through quality sleep, targeted nutrition, active recovery, and stress management, even with demanding schedules.

Discover the key principles and actionable strategies for structuring your workouts to maximize rapid strength gains, focusing on progressive overload, frequency, volume, and periodization.
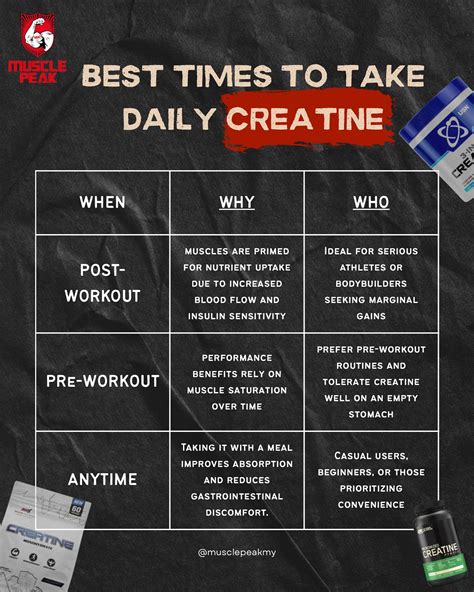
For those with demanding schedules, unlocking peak muscle and power gains requires a strategic, time-efficient approach centered on compound movements, high intensity, and smart recovery.
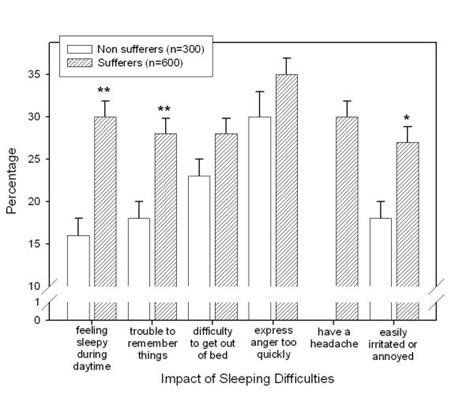
Inconsistent sleep quality significantly hinders men’s strength gains by disrupting crucial anabolic hormones, impairing muscle recovery and repair, and inducing central nervous system fatigue, thereby diminishing training performance and long-term progress.

Men often face two critical pitfalls when trying to increase their squat maximum: compromising proper form for heavier weight and adopting an ineffective training frequency that either under-stimulates or over-stresses the body, both hindering strength gains and increasing injury risk.