
Best workout split for optimal hypertrophy and strength gains for busy men?
Discover the most effective workout splits for busy men aiming to maximize muscle growth and strength gains without sacrificing their packed schedules.

Discover the most effective workout splits for busy men aiming to maximize muscle growth and strength gains without sacrificing their packed schedules.

Discover the most effective workout splits designed to maximize male strength and muscle growth, analyzing popular methods like Full Body, Upper/Lower, and PPL, alongside key training principles.

Discover key strategies and scientific principles for optimizing your strength training routines to achieve maximum muscle growth and peak performance efficiently.

Discover how to maximize muscle growth and strength even with a busy schedule by focusing on intelligent programming, compound movements, high intensity, and efficient time management.
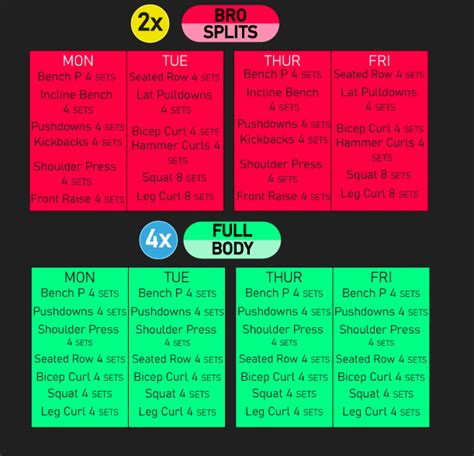
Discover how to choose the perfect workout split that harmonizes the demands of building peak strength, maximizing muscle growth, and ensuring adequate recovery for sustainable progress.

Discover how to optimize your training sessions to build significant muscle and strength, even when you have limited time, by focusing on intensity, smart exercise selection, and advanced training techniques.

Discover advanced training strategies and lifestyle adjustments to break through stubborn muscle growth plateaus and achieve optimal hypertrophy, from progressive overload variations to high-intensity techniques and crucial recovery insights.

Achieving peak strength and significant hypertrophy requires a meticulously structured workout plan that incorporates progressive overload, optimized volume, frequency, and strategic recovery tailored to individual goals.

Discover the most effective workout splits, from full-body to Push/Pull/Legs, that balance frequency, volume, and recovery to maximize both strength and muscle growth.

Discover how men can effectively fine-tune their training volume to maximize muscle growth, enhance strength, and improve overall athletic performance through strategic programming and recovery.