Optimize gym time: HIIT vs. traditional lifting for peak performance?

For anyone stepping into a gym, a common question arises: how can I make the most of my limited time to achieve optimal results? The fitness world offers a plethora of approaches, but two methods consistently stand out for their effectiveness and dedicated following: High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and traditional weightlifting. Both promise significant gains, but they approach fitness from different angles. Understanding their unique benefits and drawbacks is crucial for tailoring a workout regimen that aligns with your specific goals for peak performance.
Understanding High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
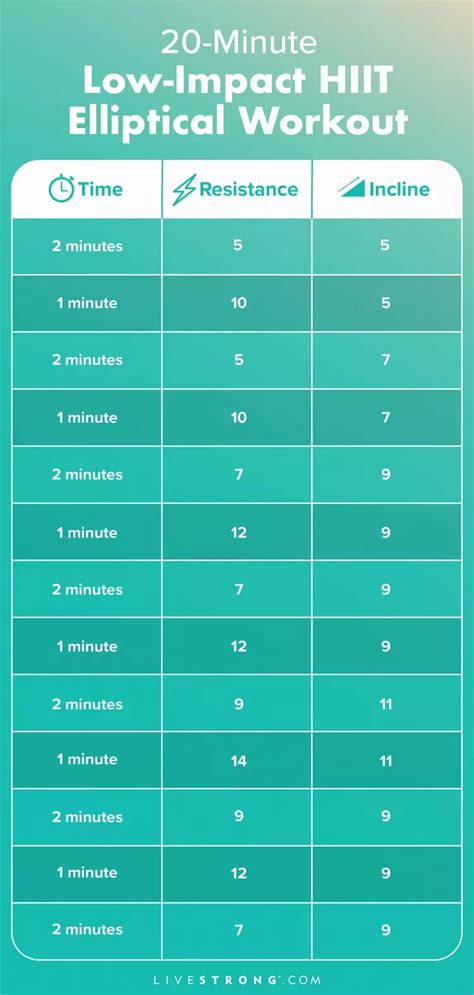
HIIT involves short bursts of intense anaerobic exercise followed by brief, often active, recovery periods. This cycle is repeated for a set number of rounds or a specific duration, typically ranging from 10 to 30 minutes. The hallmark of HIIT is its maximal effort during the work intervals, pushing your heart rate to near its maximum capacity.
The appeal of HIIT lies primarily in its time efficiency. Despite shorter workout durations, studies show it can lead to significant improvements in cardiovascular fitness, endurance, and fat loss. The “afterburn effect,” or Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC), means your body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate even after your workout is over, aiding in sustained fat metabolism. Exercises commonly used in HIIT include sprints, burpees, jump squats, and battle ropes.
The Foundations of Traditional Weightlifting
In contrast, traditional weightlifting, often synonymous with strength training, focuses on lifting weights with controlled movements to build muscle mass, increase strength, and improve bone density. This typically involves sets and repetitions of exercises targeting specific muscle groups, with adequate rest periods between sets. Programs are often structured around progressive overload, where the weight, reps, or volume are gradually increased over time to continually challenge the muscles.
Traditional lifting is highly effective for promoting muscle hypertrophy (growth) and developing raw strength. It’s the cornerstone for bodybuilders, powerlifters, and anyone looking to significantly alter their body composition by increasing lean muscle mass. Beyond aesthetics and strength, it also plays a vital role in improving functional movement, reducing the risk of injury, and boosting metabolism through increased muscle mass.

Comparing HIIT and Traditional Lifting: Key Metrics
When choosing between HIIT and traditional lifting, it’s helpful to compare them across several key performance indicators:
- Time Efficiency: HIIT generally wins for shorter session times, often delivering impressive results in under 30 minutes. Traditional lifting sessions typically require 45-90 minutes, including warm-up, cool-down, and rest between sets.
- Muscle Growth & Strength: Traditional weightlifting is unequivocally superior for maximizing muscle hypertrophy and absolute strength gains due to its focus on progressive overload and specific muscle targeting. While HIIT can build some muscle, it’s not its primary strength.
- Fat Loss: Both are effective. HIIT excels in burning a high number of calories in a short period and creating a significant EPOC effect. Traditional lifting boosts your basal metabolic rate long-term by increasing muscle mass, which burns more calories at rest.
- Cardiovascular Health: HIIT is a powerhouse for improving cardiorespiratory fitness quickly. Traditional lifting, especially with shorter rest periods, can also provide cardiovascular benefits, but not to the same extent as dedicated HIIT.
- Injury Risk & Recovery: Both carry risks if not performed correctly. The high-impact and explosive nature of some HIIT exercises can be challenging for beginners or those with pre-existing conditions. Traditional lifting, with proper form, can be very safe, but heavy loads require strict technique to prevent injury. Recovery time is generally longer for traditional lifting, especially after heavy sessions.

Choosing Your Path or Combining Both
The “best” method truly depends on your individual goals:
- Choose HIIT if: Your primary goals are significant fat loss, improving cardiovascular endurance quickly, or if you have very limited time for workouts.
- Choose Traditional Lifting if: Your focus is on building substantial muscle mass, increasing strength, improving bone density, or achieving a more sculpted physique.
However, for many, the optimal approach isn’t an “either/or” but a “both/and.” A hybrid approach that incorporates elements of both HIIT and traditional lifting can offer the best of both worlds. For example, you might dedicate 2-3 days a week to strength training and 1-2 days to HIIT sessions. This synergistic combination allows for muscle building and strength development while also enhancing cardiovascular fitness and accelerating fat loss.

Maximizing Your Gym Time for Peak Performance
Regardless of the method you choose, consistency, proper form, and adequate nutrition are paramount. Listen to your body, incorporate rest and recovery, and adjust your program as your goals evolve. For peak performance, it’s not just about what you do, but how you do it, and how well it fits into your overall lifestyle and long-term aspirations.

Ultimately, both HIIT and traditional lifting are powerful tools in your fitness arsenal. By understanding their distinct advantages, you can make an informed decision to optimize your gym time, whether that means focusing on one, or strategically combining them to forge a well-rounded path towards peak physical performance and a healthier, stronger you.







