How does adequate dietary zinc intake specifically contribute to men’s reproductive and immune health?

Zinc, an essential trace mineral, is a fundamental component for numerous physiological processes within the human body. While its importance for overall health is widely recognized, its specific contributions to men’s reproductive and immune health are particularly significant. This often-overlooked nutrient acts as a cofactor for over 300 enzymes, influencing everything from DNA synthesis to protein metabolism. For men, ensuring an adequate intake of zinc is not just about general well-being; it’s about safeguarding critical systems that define vitality and resilience.

Zinc’s Profound Impact on Male Reproductive Health
The role of zinc in male reproductive health is multifaceted and critical. It is highly concentrated in the testes and prostate gland, underscoring its importance in these organs. One of its primary functions is its involvement in spermatogenesis, the process of sperm production. Adequate zinc levels are necessary for the development and maturation of healthy sperm, influencing their motility, morphology, and overall viability. Deficiencies can lead to impaired sperm quality, reduced sperm count, and an increased risk of male infertility.
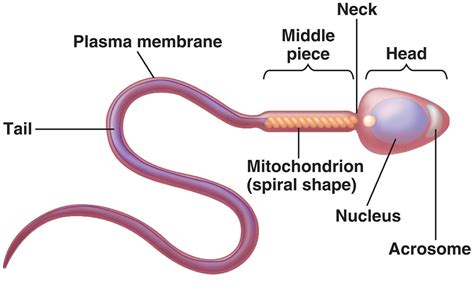
Beyond sperm production, zinc also plays a crucial role in regulating testosterone levels. It is involved in the synthesis and secretion of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. Studies have shown a correlation between low zinc levels and reduced testosterone, while zinc supplementation in deficient men can help normalize these hormone levels. Maintaining optimal testosterone is vital not only for libido and sexual function but also for muscle mass, bone density, and mood regulation.

Furthermore, zinc acts as a powerful antioxidant within the reproductive system. It helps protect sperm cells from oxidative stress, which can cause DNA damage and impair sperm function. By mitigating the effects of free radicals, zinc contributes to the structural integrity of sperm and the health of the reproductive tissues.
Strengthening the Immune System with Zinc
Zinc is indispensable for a robust immune system. It influences both innate and adaptive immunity, making it a critical nutrient for defending the body against pathogens. Zinc is essential for the development and function of immune cells, including T-lymphocytes (T-cells) and B-lymphocytes (B-cells), which are central to the body’s specific immune responses. It also plays a role in the activity of natural killer cells and macrophages, frontline defenders against infections.

Adequate zinc intake helps modulate inflammatory responses, preventing both excessive inflammation that can damage tissues and insufficient inflammation that can allow infections to proliferate. Its antioxidant properties extend to immune cells, protecting them from damage during active immune responses. A deficiency in zinc can lead to impaired immune function, making individuals more susceptible to infections, experiencing longer recovery times, and having a reduced ability to mount an effective immune response.
Beyond preventing illness, zinc is also vital for wound healing. It is involved in every stage of the wound healing process, from coagulation and inflammation to cell proliferation and tissue remodeling. Ensuring sufficient zinc intake can accelerate recovery from injuries and infections, further highlighting its comprehensive role in immune resilience.
Achieving Optimal Zinc Intake
For adult men, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for zinc is 11 milligrams (mg). Fortunately, many common foods are excellent sources of this vital mineral. Oysters are exceptionally rich in zinc, but red meat (beef, lamb), poultry, beans, nuts (especially cashews and almonds), whole grains, and dairy products also contribute significantly. For individuals with dietary restrictions or specific health conditions that may impair zinc absorption, supplementation might be considered, but always under the guidance of a healthcare professional.

Incorporating a variety of these zinc-rich foods into a balanced diet is the most effective way to ensure consistent and adequate intake. Cooking methods and other dietary components can influence zinc bioavailability, so a diverse diet is key to maximizing absorption and utilization.
Conclusion
In summary, zinc is far more than just another mineral; it’s a cornerstone of men’s health, particularly concerning reproduction and immunity. From orchestrating spermatogenesis and maintaining optimal testosterone levels to bolstering the immune system’s cellular defenses and fighting oxidative stress, its influence is pervasive and profound. Prioritizing adequate dietary zinc intake through a balanced and nutrient-dense diet is an essential strategy for men seeking to optimize their reproductive vitality and maintain a resilient, responsive immune system throughout life.









