Best progressive overload strategy to maximize strength & growth?

Understanding the Core Principle of Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the fundamental principle behind all successful strength training programs. Simply put, it means continually increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. Without this constant challenge, your body has no reason to adapt by getting stronger or growing larger. It’s the driving force that pushes your body beyond its current capabilities, forcing it to build more resilient muscle tissue and neurological efficiency.
Many lifters plateau because they fail to consistently apply this principle. They perform the same exercises with the same weights and reps for too long. To maximize strength and growth, you must strategically manipulate variables in your training.

Key Strategies for Progressive Overload
Progressive overload isn’t just about adding more weight to the bar. There are multiple dimensions you can adjust to keep your muscles adapting:
1. Increase the Load (Weight)
This is the most common and often most effective method, especially for strength gains. Once you can comfortably perform your target reps with good form, it’s time to increase the weight. Even a small increase (e.g., 2.5 lbs or 1 kg) can be enough to stimulate further adaptation.
2. Increase Repetitions
If increasing the weight isn’t feasible or desired for a particular exercise, aim for more reps within your target range (e.g., going from 8 to 10 reps). Once you hit the upper end of your rep range for a given weight, then consider increasing the weight.
3. Increase Sets (Volume)
Performing an additional set for an exercise or muscle group can significantly increase your total training volume, stimulating more growth. Be mindful not to add too many sets, as this can lead to overtraining and hinder recovery.

4. Decrease Rest Intervals
Reducing the time you rest between sets makes the subsequent sets harder, increasing the metabolic stress on your muscles. This is particularly effective for hypertrophy (muscle growth) and improving muscular endurance. Be cautious not to reduce rest so much that it compromises your ability to lift challenging weights.
5. Improve Form and Technique
While not a direct increase in external load, improving your lifting technique allows you to recruit more muscle fibers and handle heavier weights more safely and efficiently. A stricter form with a greater mind-muscle connection can make a lighter weight feel heavier and more challenging, leading to better stimulation.
6. Increase Time Under Tension (TUT)
This involves controlling the eccentric (lowering) and concentric (lifting) phases of an exercise. Slower, more controlled movements, especially during the eccentric phase, can increase the time your muscles are under tension, leading to greater muscle damage and subsequent growth. For example, taking 3-4 seconds to lower a weight.

7. Increase Training Frequency or Density
Training a muscle group more often throughout the week (frequency) or completing the same amount of work in less time (density) can also be forms of progressive overload. This approach requires careful programming to ensure adequate recovery.
Tailoring Strategies for Strength vs. Hypertrophy
While progressive overload is vital for both strength and growth, the emphasis on certain strategies might shift:
- For Strength: Prioritize increasing the load (weight) and maintaining excellent form. Focusing on lower rep ranges (1-6) with heavier weights is key. Periodically, you might also increase sets or frequency for specific lifts.
- For Hypertrophy: Focus on increasing total volume (sets x reps x weight). This can involve increasing reps, sets, decreasing rest intervals, and increasing time under tension. Rep ranges from 6-12 are typically favored, but effective hypertrophy can occur across a broader range when volume is adequate.
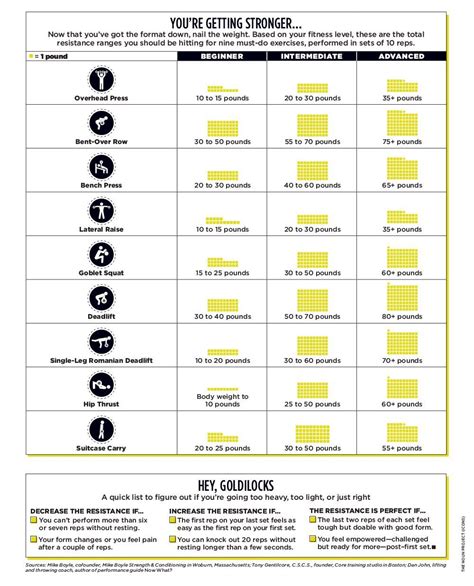
Implementing Progressive Overload Effectively
To successfully apply progressive overload, consistency and tracking are paramount:
- Track Everything: Keep a log of your exercises, sets, reps, and weights. This is crucial for knowing what you did last time and how to beat it.
- Micro-Load: Don’t wait for large jumps. Utilize fractional plates (0.5 kg or 1.25 lb) to make smaller, more consistent increases in weight.
- Prioritize Form: Never sacrifice good form for more weight or reps. Poor form increases injury risk and reduces muscle activation.
- Listen to Your Body: Some days you’ll feel stronger than others. It’s okay to have off days or slightly lighter sessions. The goal is long-term progression, not beating every single workout.
- Strategic Deloads: Periodically, reduce your training volume or intensity for a week (a deload week). This allows your body to fully recover and prepares you for further progress.
- Periodization: Systematically varying your training volume, intensity, and exercise selection over time can prevent plateaus and optimize long-term gains.

Conclusion
The best progressive overload strategy isn’t a single method but rather a thoughtful and consistent application of various techniques. By continually challenging your muscles through increased weight, reps, sets, improved form, or strategic rest reductions, you provide the necessary stimulus for ongoing strength and muscle growth. Track your progress, be patient, and remember that consistency in effort and strategy is the ultimate key to maximizing your gains.







