What diet optimizes testosterone naturally for men’s performance?

Testosterone, often hailed as the cornerstone of male vitality, plays a crucial role not only in reproductive health but also in muscle mass, bone density, mood, energy levels, and overall athletic and cognitive performance. While various factors influence its production, diet stands out as one of the most powerful and modifiable levers men can pull to naturally optimize their testosterone levels. Shifting towards a nutrient-dense eating pattern can support hormonal balance, enhance physical capabilities, and improve quality of life.
The Foundational Pillars of a T-Optimizing Diet
A successful diet for testosterone optimization isn’t about restrictive fads but rather a balanced intake of macronutrients—fats, proteins, and carbohydrates—sourced from whole, unprocessed foods.
Prioritize Healthy Fats
Contrary to outdated beliefs, healthy fats are essential for testosterone production. Cholesterol, a precursor to testosterone, is synthesized from dietary fats. Incorporate a variety of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats:
- Monounsaturated Fats: Found in avocados, olive oil, nuts (almonds, cashews), and seeds.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are particularly beneficial for overall hormonal health and reducing inflammation.

Adequate Protein Intake
Protein is vital for muscle repair and growth, which indirectly supports healthy testosterone levels, especially when combined with resistance training. Aim for lean protein sources that also provide essential amino acids:
- Lean meats (beef, chicken, turkey)
- Fish and seafood
- Eggs
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Dairy products (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese)
Complex Carbohydrates for Sustained Energy
While low-carb diets have their place, overly restrictive carbohydrate intake can negatively impact testosterone, particularly for active men. Complex carbohydrates provide the energy needed for workouts and daily functions, preventing the body from entering a stress state that can suppress hormone production.
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice, whole-wheat bread)
- Fruits (berries, apples, bananas)
- Starchy vegetables (sweet potatoes, pumpkin)

Key Micronutrients for Testosterone Production
Beyond macronutrients, specific vitamins and minerals play direct roles in the enzymatic processes involved in testosterone synthesis.
Zinc: The Mineral for Male Hormones
Zinc is perhaps one of the most crucial minerals for testosterone. Deficiency is directly linked to reduced testosterone levels. It’s involved in nearly every aspect of male reproductive health.
- Rich sources include oysters, red meat, poultry, pumpkin seeds, spinach, and legumes.
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
Often acting more like a hormone than a vitamin, Vitamin D is strongly correlated with testosterone levels. Many men are deficient, especially in regions with less sunlight.
- Get adequate sun exposure safely, or supplement under guidance.
- Dietary sources include fatty fish (salmon, tuna), fortified dairy, and egg yolks.

Magnesium: Muscle and Hormone Support
Magnesium plays a role in hundreds of bodily reactions, including those that support testosterone. It can reduce sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), making more free testosterone available.
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds, and whole grains are excellent sources.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Just as important as what you eat is what you limit or avoid. Certain foods can actively suppress testosterone or contribute to an unhealthy body composition that hinders hormone production.
- Processed Foods and Refined Sugars: These lead to insulin resistance and inflammation, both detrimental to hormone health.
- Excessive Alcohol: Can increase estrogen and decrease testosterone.
- Trans Fats and Unhealthy Saturated Fats: Found in fried foods and many packaged snacks, these contribute to poor cardiovascular health and can negatively impact hormone function.
- Soy Products (in excess): While moderate consumption is fine for most, very high intake of soy isoflavones might potentially interfere with hormone balance for some individuals, though research is mixed.

Hydration and Lifestyle Factors
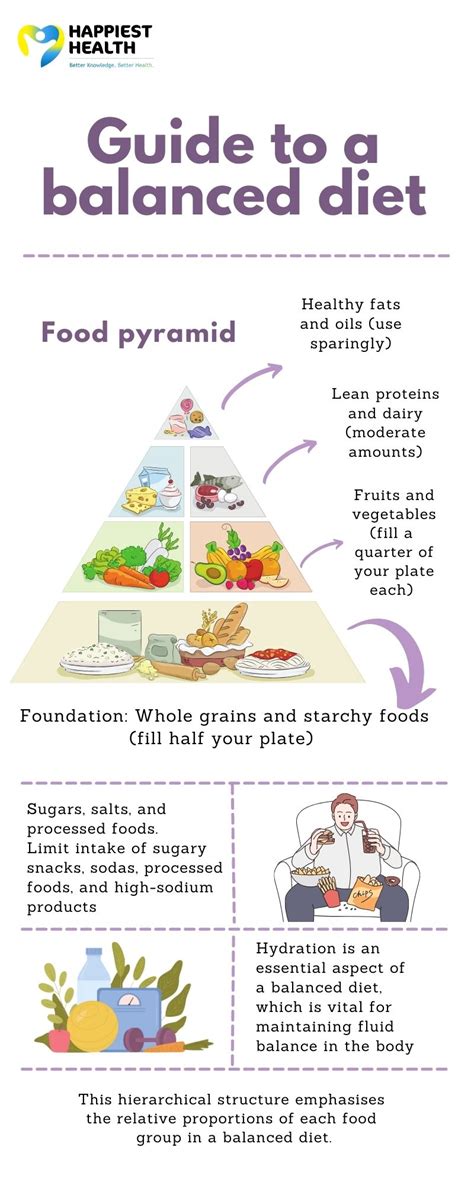
Beyond specific food choices, maintaining proper hydration is fundamental for all bodily functions, including hormone synthesis and transport. Drinking sufficient water throughout the day supports metabolic processes and overall well-being.
While the focus here is diet, it’s crucial to remember that diet works synergistically with other lifestyle factors. Regular exercise (especially strength training), adequate sleep (7-9 hours), and effective stress management are equally vital components in the holistic approach to naturally optimizing testosterone and enhancing men’s performance.
Conclusion
Optimizing testosterone naturally through diet is an achievable goal for men seeking to enhance their performance and overall health. By focusing on a balanced intake of healthy fats, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates, alongside a rich supply of zinc, vitamin D, and magnesium, men can create a powerful dietary foundation. Avoiding processed foods, excessive sugars, and unhealthy fats further strengthens this approach. Remember, consistency is key, and integrating these dietary principles into a holistic healthy lifestyle will yield the most profound and lasting benefits for vitality and performance.








