What is the optimal daily protein intake range recommended for men aiming to build and maintain muscle mass?

Understanding Protein’s Role in Muscle Growth
For men dedicated to building and maintaining muscle mass, protein is not merely a nutrient; it’s the fundamental building block. Every strenuous workout session causes micro-tears in muscle fibers. Protein provides the essential amino acids needed to repair these tears and synthesize new muscle tissue, a process known as muscle protein synthesis (MPS). Without adequate protein, the body struggles to recover effectively, leading to suboptimal gains and even muscle loss.
The Optimal Daily Protein Intake Range
While general dietary guidelines recommend a certain amount of protein for overall health, men actively engaged in resistance training and aiming for significant muscle development require significantly more. Research consistently points to a range that optimizes MPS and supports hypertrophy (muscle growth).

The generally accepted optimal range for men looking to build and maintain muscle mass is 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day (g/kg/day). For individuals who prefer imperial units, this translates to approximately 0.7 to 1.0 gram of protein per pound of body weight per day (g/lb/day).
- 1.6 g/kg (0.7 g/lb): This is often considered the minimum effective dose for maximizing MPS in resistance-trained individuals.
- 2.2 g/kg (1.0 g/lb): This upper end of the range offers additional benefits for muscle retention during caloric deficits (cutting phases) and may provide a slight edge for muscle growth in bulking phases, though benefits beyond this point tend to diminish.
Factors Influencing Your Protein Needs
While the 1.6-2.2 g/kg range is a strong guideline, individual needs can vary based on several factors:
Training Intensity and Volume
The more intensely and frequently you train, the greater the demand on your muscles for repair and growth, thus potentially increasing your protein requirement towards the higher end of the spectrum.
Body Composition Goals
If you are in a caloric deficit to lose fat, a higher protein intake (closer to 2.0-2.2 g/kg) is crucial for preserving lean muscle mass. During a caloric surplus (bulking), adequate protein ensures the gained weight is primarily muscle, not just fat.

Age
As men age, anabolic resistance can occur, meaning the body becomes less efficient at utilizing protein for muscle protein synthesis. Older men may benefit from slightly higher protein intakes (e.g., closer to 2.0-2.2 g/kg) to counteract this and maintain muscle mass.
Overall Diet
The presence of sufficient carbohydrates and fats in your diet can influence how protein is utilized. Adequate energy intake prevents the body from using protein as a primary energy source, reserving it for its crucial role in muscle repair and growth.
Strategic Protein Distribution and Sources
Meeting your daily protein target isn’t just about the total amount; it’s also about how you distribute it throughout the day and the quality of your sources.
Even Distribution
Aim to consume protein every 3-4 hours, with each meal containing 20-40 grams (or more, depending on your total daily target). This ensures a steady supply of amino acids, consistently stimulating muscle protein synthesis.
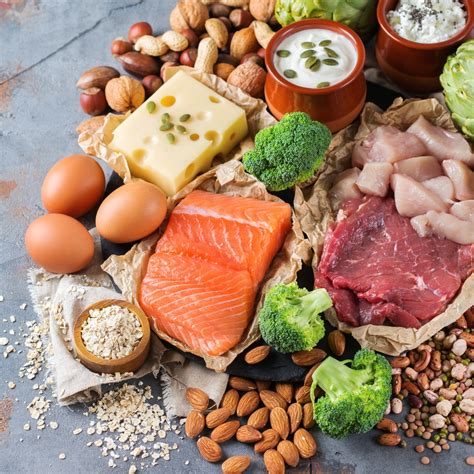

High-Quality Protein Sources
Focus on complete protein sources that provide all essential amino acids:
- Animal-based: Lean beef, chicken, turkey, fish (salmon, tuna), eggs, dairy (milk, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, whey protein).
- Plant-based: Soy products (tofu, tempeh, edamame), quinoa, lentils, beans, chickpeas, nuts, seeds, and plant-based protein powders (pea, rice, hemp). A combination of various plant proteins throughout the day can ensure a complete amino acid profile.
Common Misconceptions and Considerations
“Too Much Protein is Bad for Your Kidneys”
For healthy individuals with no pre-existing kidney conditions, a high protein intake within the recommended range has not been shown to cause kidney damage. However, individuals with kidney disease should consult a doctor before increasing protein intake.
Focus on Whole Foods
While protein supplements can be convenient, prioritize obtaining the majority of your protein from whole, unprocessed foods, which also provide a wealth of other essential micronutrients.

Conclusion
For men serious about building and maintaining muscle mass, a daily protein intake ranging from 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram (0.7-1.0 g/lb) of body weight is the scientifically supported optimal range. Distributing this intake across multiple meals throughout the day, focusing on high-quality protein sources, and considering individual factors like training intensity and age, will significantly enhance your efforts in achieving your muscle-building goals. Remember, consistency is key, both in your training and your nutritional approach.