Which micronutrients are most crucial for supporting healthy testosterone levels in men?
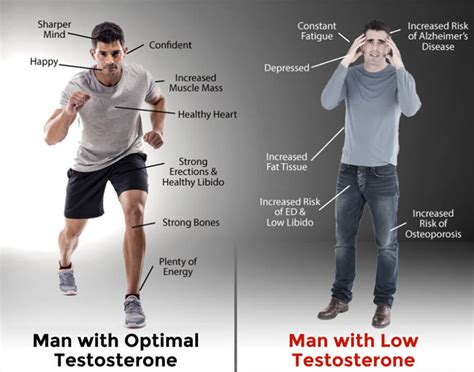
Testosterone, often called the primary male sex hormone, is fundamental to men’s health, influencing everything from muscle mass and bone density to mood, energy levels, and libido. While various factors contribute to healthy testosterone production, a balanced intake of specific micronutrients stands out as particularly crucial. Deficiencies in these essential vitamins and minerals can directly impair the body’s ability to synthesize and regulate this vital hormone.
The Cornerstone Micronutrients for Testosterone Support
Several vitamins and minerals are directly involved in the intricate pathways of testosterone synthesis and function. Focusing on these can be a powerful strategy for maintaining optimal levels.

1. Zinc: The Essential Mineral
Zinc is arguably one of the most vital minerals for testosterone production. It’s involved in numerous enzymatic processes, including those that regulate the production of luteinizing hormone (LH), which signals the testes to produce testosterone. Studies have shown that zinc deficiency can lead to decreased testosterone levels, and supplementation in deficient individuals can significantly improve them. Zinc also plays a role in preventing the aromatization of testosterone into estrogen, further preserving healthy levels.
Excellent dietary sources include oysters, red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and dairy products.

2. Vitamin D: The Sunshine Hormone
Often referred to as a pro-hormone, Vitamin D plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including endocrine health. Research consistently links higher Vitamin D levels with higher testosterone levels in men. It’s believed that Vitamin D receptors are present on testicular Leydig cells, which are responsible for testosterone production. Adequate sunlight exposure is the primary way to obtain Vitamin D, but dietary sources like fatty fish, fortified foods, and supplements are also important, especially in regions with limited sun.
3. Magnesium: The Muscle and Hormone Ally
Magnesium is another mineral indispensable for overall health, and its impact on testosterone is noteworthy. It helps in the bioavailability of testosterone by reducing its binding to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). When testosterone is bound to SHBG, it’s considered inactive. By reducing SHBG, magnesium ensures more free, active testosterone is available in the body. Furthermore, magnesium is crucial for muscle function and energy production, both of which are indirectly related to hormonal health.
Rich sources include dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and dark chocolate.

4. Boron: The Lesser-Known Booster
While not as widely discussed as zinc or Vitamin D, boron is gaining recognition for its potential role in testosterone support. Studies suggest that boron can increase free testosterone levels by reducing SHBG and may also reduce estrogen levels. It also aids in Vitamin D absorption and magnesium utilization, amplifying the benefits of these other critical micronutrients.
Boron can be found in fruits (especially apples, pears, and grapes), vegetables, nuts, and legumes.
5. Selenium: Antioxidant and Hormone Support
Selenium is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells, including those in the testes, from oxidative damage. While its direct impact on testosterone is less pronounced than zinc or Vitamin D, adequate selenium is essential for overall endocrine function and sperm quality, indirectly supporting reproductive health and hormone balance.
Brazil nuts, seafood, organ meats, and whole grains are good sources of selenium.

Beyond the Key Players
While zinc, Vitamin D, magnesium, boron, and selenium are central, other micronutrients like Vitamin K2, Omega-3 fatty acids, and certain B vitamins also contribute to overall hormonal health and testosterone production indirectly. A holistic approach to nutrition, emphasizing a wide variety of whole foods, is always the best strategy.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy testosterone levels is a multifaceted endeavor, and nutrition plays a foundational role. By ensuring adequate intake of crucial micronutrients like zinc, Vitamin D, magnesium, and boron, men can significantly support their body’s natural ability to produce and regulate this vital hormone. While diet should always be the primary source, supplementation may be considered under professional guidance, especially if deficiencies are confirmed. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen.









