What specific nutritional strategies are recommended for men over 40 to effectively mitigate age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia)?

As men cross the threshold into their 40s and beyond, a natural physiological process known as sarcopenia begins to accelerate. This age-related decline in muscle mass, strength, and function can significantly impact quality of life, increasing risks of falls, reducing metabolic rate, and affecting overall vitality. While regular resistance training is paramount, nutrition plays an equally critical, often underestimated, role in effectively slowing and even reversing this decline. Adopting specific dietary strategies can provide the building blocks and signals necessary to preserve and build muscle, ensuring men remain strong and active well into their later years.
Prioritizing High-Quality Protein Intake
Protein is the cornerstone of muscle health. For men over 40, the recommended daily protein intake often needs to be higher than younger adults to counteract anabolic resistance – a reduced muscle response to protein. Aim for approximately 1.2 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. More importantly, focus on distributing this intake evenly throughout the day, aiming for 25-40 grams of high-quality protein at each main meal.
Excellent sources of complete protein include lean meats (chicken, beef, turkey), fish (salmon, tuna), eggs, dairy products (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese), and plant-based options like soy, quinoa, and legumes when combined appropriately. Prioritizing protein immediately after resistance training can also optimize muscle repair and growth.

The Critical Role of Leucine and Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
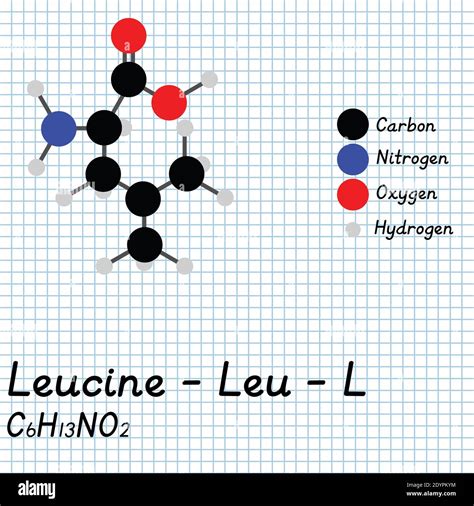
Among the amino acids, leucine stands out as a powerful stimulator of muscle protein synthesis (MPS). It acts as a trigger for the mTOR pathway, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. Ensuring sufficient leucine intake at each meal is vital for older adults. Aim for 2.5-3 grams of leucine per meal to maximize the MPS response. Foods rich in leucine include whey protein, beef, chicken, fish, eggs, and dairy products. While supplements containing BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine, valine) are available, obtaining leucine through whole food sources or a high-quality whey protein supplement is generally preferred.

Ensuring Adequate Vitamin D and Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Beyond protein, several micronutrients are crucial for muscle health. Vitamin D, often associated with bone health, also plays a significant role in muscle function, strength, and overall physical performance. Deficiency is common, especially in older adults. Regular sun exposure, fortified foods (milk, cereals), and fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) are good sources. Supplementation may be necessary, but always consult a healthcare professional for appropriate dosing.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA found in fatty fish, possess potent anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic low-grade inflammation can contribute to muscle breakdown. Omega-3s may help mitigate this inflammation, support cellular health, and potentially enhance muscle protein sensitivity, indirectly aiding in muscle preservation. Include fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel in your diet a few times a week, or consider an omega-3 supplement.
Embracing a Nutrient-Dense Whole Food Diet
While specific nutrients are highlighted, the overall quality of your diet cannot be overstated. A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods provides a spectrum of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber essential for overall health, energy levels, and metabolic function. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. These foods contribute to a healthy gut microbiome, reduce oxidative stress, and provide sustained energy for both daily activities and exercise. Adequate hydration is also fundamental for cellular function and nutrient transport.

Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Muscle Health
Mitigating sarcopenia in men over 40 requires a multi-faceted approach, with nutrition being a cornerstone. By strategically increasing high-quality protein, focusing on leucine-rich foods, ensuring adequate intake of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, and embracing a diverse whole-food diet, men can create an optimal internal environment for muscle preservation and growth. Remember that these nutritional strategies are most effective when combined with regular resistance training and a healthy, active lifestyle. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to individual needs and health conditions.