Boost natural testosterone via diet for enhanced performance?

Understanding Testosterone and Performance
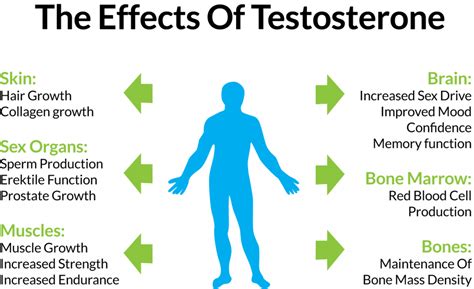
Testosterone, often dubbed the ‘male hormone,’ plays a pivotal role far beyond just sex drive. It’s a critical anabolic hormone influencing muscle growth, bone density, fat distribution, red blood cell production, and even mood and cognitive function. For anyone aiming for enhanced physical performance, better recovery, or just general vitality, maintaining optimal testosterone levels is key.
While various factors impact testosterone, including age, lifestyle, and genetics, diet stands out as a powerful and controllable lever. The foods we consume provide the building blocks and regulatory signals for hormone synthesis. By making informed nutritional choices, it’s possible to support your body’s natural testosterone production.
Essential Nutrients for Testosterone Production
Certain vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients are indispensable for healthy testosterone synthesis. Incorporating these into your daily diet can make a tangible difference.
Zinc-Rich Foods
Zinc is a crucial mineral directly involved in testosterone production. Studies have shown that even mild zinc deficiency can lead to decreased testosterone levels. Excellent dietary sources include red meat, poultry, shellfish (especially oysters), beans, nuts, seeds (pumpkin seeds are particularly good), and whole grains.
Vitamin D (The ‘Sunshine Vitamin’)
Often referred to as a hormone itself, Vitamin D is strongly correlated with testosterone levels. Research indicates that men with adequate Vitamin D levels tend to have higher testosterone. While sun exposure is the primary way to get Vitamin D, dietary sources include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), fortified milk, orange juice, and cereals. Supplementation might be necessary for many, especially in regions with limited sunlight.

Healthy Fats
Cholesterol, a type of fat, is the precursor to testosterone. Therefore, ensuring a healthy intake of good fats is vital. Focus on monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in avocados, olive oil, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia, flax), and fatty fish. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats, though some saturated fat from healthy sources like grass-fed meat or coconut oil can be beneficial in moderation.
Micronutrients and Hormone Balance
Beyond the major players, several other nutrients contribute to a healthy hormonal environment, supporting testosterone production indirectly.
Magnesium
Magnesium is another mineral that has been linked to higher testosterone levels, particularly in active individuals. It helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can negatively impact hormone production. Rich sources include leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Oxidative stress can damage cells, including those involved in hormone production. A diet rich in antioxidants helps combat this. Load up on a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables like berries, pomegranates, spinach, broccoli, and bell peppers to protect your cells and support overall hormonal health.

Cruciferous Vegetables for Estrogen Balance
While boosting testosterone, it’s also important to manage estrogen levels, as an imbalance can negate the benefits of higher T. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage contain compounds (like indole-3-carbinol) that help the body metabolize estrogen more efficiently, promoting a healthier testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
Foods to Limit for Optimal Testosterone
Just as important as what you eat is what you avoid or limit. Certain dietary choices can actively work against your efforts to boost natural testosterone.
Processed Foods and Sugary Drinks
Diets high in processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars can lead to insulin resistance, inflammation, and increased fat storage, all of which are detrimental to testosterone levels. These foods often lack essential nutrients and contribute to a poor metabolic state.

Excessive Alcohol and Unhealthy Fats
Chronic and excessive alcohol consumption is known to impair testosterone production. Similarly, a diet high in trans fats and certain unhealthy saturated fats can negatively impact hormonal health. Opt for moderation when it comes to alcohol and choose healthy fat sources.
Beyond Diet: A Holistic Approach
While diet is a cornerstone, remember that it’s part of a larger picture. To truly optimize your natural testosterone levels and performance, consider these complementary lifestyle factors:
- Regular Exercise: Especially strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can significantly boost testosterone.
- Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep quality and insufficient duration can dramatically lower testosterone. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can suppress testosterone production. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
Conclusion
Boosting natural testosterone through diet is a powerful, sustainable, and health-promoting strategy for enhancing performance and overall well-being. By prioritizing zinc, Vitamin D, healthy fats, magnesium, and a variety of antioxidant-rich whole foods, while simultaneously limiting processed items and excessive alcohol, you create an optimal environment for your body’s hormonal system. Combine these dietary strategies with smart exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management, and you’ll be well on your way to unlocking your full potential.








