What is the specific connection between adequate dietary zinc intake and male fertility?
Male fertility is a complex biological process influenced by numerous factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and critically, nutrition. Among the essential trace minerals, zinc stands out for its profound and multifaceted role in supporting male reproductive health. Often overlooked, maintaining adequate dietary zinc intake is not merely beneficial; it is a fundamental requirement for optimal fertility outcomes in men.
The Crucial Role of Zinc in Sperm Development
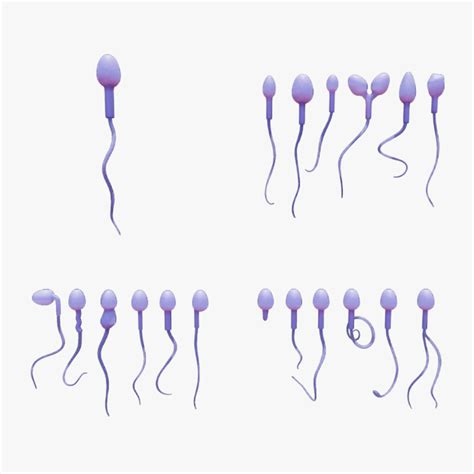
Zinc plays a direct and indispensable role in spermatogenesis, the process of sperm production. This mineral is heavily concentrated in the male reproductive system, particularly in the testes and seminal fluid. It is essential for the structural integrity of sperm cells, contributing to the formation of the outer membrane and the flagellum, which is vital for sperm motility. A deficiency in zinc can lead to impaired sperm morphology (abnormal shape), reduced sperm count, and decreased progressive motility, all of which are significant contributors to male infertility.
Furthermore, zinc is involved in DNA synthesis and repair. Given that sperm carry half of the genetic material for a new organism, maintaining the integrity of sperm DNA is paramount. Zinc acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in these processes, thereby protecting the genetic material within the sperm from damage, which could otherwise lead to chromosomal abnormalities and compromised embryo development.
Zinc’s Influence on Hormonal Balance
Beyond its direct impact on sperm, zinc is a key player in the regulation of male reproductive hormones, most notably testosterone. It is involved in the enzymatic processes that convert androgens into testosterone. Research indicates that low zinc levels can lead to reduced testosterone production, which in turn can negatively affect libido, sperm production, and overall reproductive function. Adequate zinc intake helps maintain optimal testosterone levels, which are crucial for the entire cascade of male fertility processes.

Moreover, zinc affects the activity of prolactin and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), both of which are critical for testicular function and sperm maturation. By ensuring proper endocrine balance, zinc indirectly supports the entire male reproductive axis, contributing to a fertile environment.
Antioxidant Protection for Sperm Health
Sperm cells are particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress due to their high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids and limited cytoplasmic antioxidant defense mechanisms. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, can damage sperm DNA, proteins, and lipids, leading to decreased motility, impaired fertilization capacity, and increased risk of recurrent pregnancy loss.

Zinc is a powerful antioxidant and an essential component of several antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD). It helps to neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce lipid peroxidation in sperm membranes. By bolstering the antioxidant defense system, zinc protects sperm from oxidative damage, thereby preserving their viability, motility, and genetic integrity—all essential factors for successful fertilization.
Dietary Sources and Recommendations
Given its critical role, ensuring sufficient zinc intake through diet is paramount for male fertility. Excellent dietary sources of zinc include:
- Red Meat: Beef, lamb, and pork are rich sources.
- Shellfish: Oysters are exceptionally high in zinc, followed by crab and lobster.
- Legumes: Chickpeas, lentils, and beans provide a good amount of zinc, though plant-based sources have lower bioavailability.
- Nuts and Seeds: Pumpkin seeds, cashews, and almonds are good options.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt contain zinc.
- Whole Grains: Oats, quinoa, and brown rice contribute to zinc intake.

The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for adult men is typically around 11 mg. However, individual needs can vary, and men with pre-existing fertility issues or dietary restrictions might benefit from professional guidance regarding supplementation. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen to ensure appropriate dosage and avoid potential interactions or side effects.
Conclusion: Zinc as a Cornerstone of Male Reproductive Health
The intricate connection between adequate dietary zinc intake and male fertility is undeniable and multifaceted. From facilitating optimal sperm production, morphology, and motility to regulating crucial reproductive hormones like testosterone and providing vital antioxidant protection against oxidative stress, zinc acts as a cornerstone for male reproductive health. Prioritizing zinc-rich foods in the diet is a proactive and fundamental step for men looking to support and enhance their fertility potential. Understanding and addressing zinc status can be a significant factor in the journey towards successful conception.









