What specific dietary compounds are most beneficial for supporting prostate health in men?
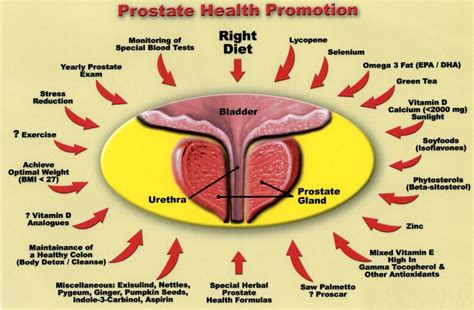
Maintaining prostate health is a significant concern for men, particularly as they age. While genetics and lifestyle play crucial roles, the foods we consume offer a powerful, proactive strategy for supporting this vital gland. Scientific research has highlighted several specific dietary compounds that exhibit remarkable benefits in promoting prostate well-being, from reducing inflammation to inhibiting cellular proliferation.
The Power of Lycopene: A Red Pigment’s Role
One of the most extensively studied dietary compounds for prostate health is lycopene, a potent antioxidant responsible for the red color in many fruits and vegetables. Found in high concentrations in tomatoes, watermelon, pink grapefruit, and guava, lycopene helps protect cells from damage by free radicals. Studies suggest that a diet rich in lycopene may be associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer and a slower progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).

Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Inflammation Fighters
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to the development and progression of prostate issues. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3s, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, can help modulate inflammatory pathways, thereby supporting prostate health.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Nature’s Protective Arsenal
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage are more than just nutrient-dense; they contain powerful compounds such as sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol (I3C). These compounds are celebrated for their ability to detoxify carcinogens, reduce oxidative stress, and influence hormone metabolism, which can be beneficial in preventing the growth of abnormal prostate cells.

Green Tea Catechins: Antioxidant and Anti-proliferative Effects
The humble green tea leaf is a treasure trove of catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). EGCG possesses strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-androgenic properties, meaning it can help inhibit the activity of hormones that fuel prostate growth. Regular consumption of green tea has been linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer and may help manage BPH symptoms.
Selenium and Zinc: Essential Trace Minerals
Two trace minerals, selenium and zinc, play distinct yet crucial roles in prostate health. Selenium, found in Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains, is a powerful antioxidant that supports DNA repair and immune function. Zinc, abundant in oysters, red meat, and pumpkin seeds, is critical for normal prostate function and has been shown to inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells in some studies, although balance is key as excessive zinc can be detrimental.

Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin’s Protective Role
Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D is increasingly recognized for its role beyond bone health, including its potential protective effects against various cancers, including prostate cancer. Adequate levels of Vitamin D are associated with a reduced risk of aggressive prostate cancer and may help regulate cell growth and differentiation. Sources include fatty fish, fortified foods, and sunlight exposure.
Phytosterols: Plant-Based Sterols for Symptom Relief
Phytosterols, plant compounds structurally similar to cholesterol, are found in nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, and legumes. Beta-sitosterol is one well-known phytosterol that has been particularly studied for its ability to alleviate symptoms of BPH, such as improved urinary flow and reduced urgency. It is believed to work by reducing inflammation and inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to prostate enlargement.

Beyond Single Compounds: A Synergistic Approach
While individual compounds offer significant benefits, the most effective strategy for prostate health involves a holistic dietary pattern. This typically includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. The synergistic action of numerous compounds working together in whole foods often surpasses the benefits of isolated supplements. Reducing processed foods, excessive red meat, and unhealthy fats also contributes significantly to overall prostate well-being.

Conclusion
Supporting prostate health through diet is a proactive and empowering approach for men. By consciously incorporating foods rich in compounds like lycopene, omega-3 fatty acids, sulforaphane, EGCG, selenium, zinc, and Vitamin D, men can contribute significantly to reducing inflammation, combating oxidative stress, and modulating hormone activity beneficial for their prostate. While diet is a powerful tool, it should always complement regular medical check-ups and a healthy lifestyle to ensure comprehensive prostate care.








