What is the primary role of Vitamin D in bone health?

The Essential Nutrient for Strong Bones
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is a fat-soluble vitamin crucial for numerous bodily functions. While its benefits extend to immune system support, cell growth, and inflammation reduction, its most well-known and primary role revolves around maintaining robust bone health. Without adequate Vitamin D, the intricate processes that keep our skeletal system strong and resilient cannot function effectively, leading to potentially severe health consequences.

Facilitating Calcium and Phosphorus Absorption
The cornerstone of Vitamin D’s contribution to bone health is its critical role in regulating the body’s calcium and phosphorus levels. These two minerals are the primary building blocks of bone tissue. Vitamin D, once converted into its active hormonal form known as calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D), acts on the small intestine to significantly enhance the absorption of dietary calcium and phosphorus.
Without sufficient calcitriol, only about 10-15% of dietary calcium and 50-60% of phosphorus are absorbed. With adequate calcitriol, these absorption rates jump dramatically to 30-40% for calcium and 80% for phosphorus. This enhanced absorption ensures that there is an ample supply of these crucial minerals circulating in the bloodstream, ready to be utilized for bone formation and mineralization.
Maintaining Mineral Homeostasis and Bone Mineralization
Beyond direct absorption, Vitamin D is a key player in maintaining calcium homeostasis – a stable balance of calcium in the blood. When blood calcium levels drop, the parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH, in turn, stimulates the kidneys to convert more inactive Vitamin D into active calcitriol. This active Vitamin D then works to:
- Increase calcium absorption from the gut.
- Reduce calcium excretion by the kidneys.
- Mobilize calcium from bone if necessary, working in conjunction with PTH.
This intricate feedback loop ensures that serum calcium levels remain within a tight, healthy range, which is vital not just for bones but also for nerve and muscle function. Consistent availability of calcium and phosphorus is essential for the process of bone mineralization, where these minerals are deposited onto the protein matrix of bones, making them hard and strong.
Consequences of Vitamin D Deficiency
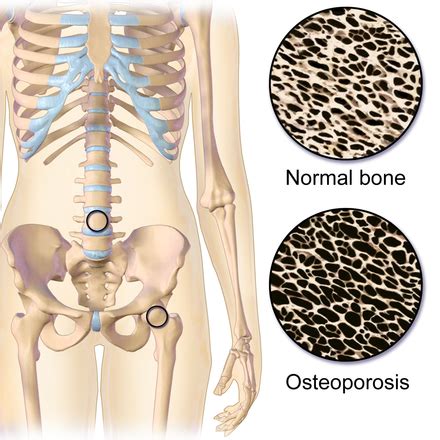
A deficiency in Vitamin D can have severe repercussions for bone health. In children, it leads to rickets, a condition characterized by soft, weak bones, impaired growth, and skeletal deformities. In adults, the deficiency results in osteomalacia, where bones become soft, weak, and prone to fractures due to inadequate mineralization.
Furthermore, chronic Vitamin D insufficiency contributes to osteoporosis, a condition marked by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk, particularly in older adults. Without enough Vitamin D to facilitate calcium absorption, the body may resort to drawing calcium from the bones to maintain blood calcium levels, further weakening the skeletal structure.
Beyond Direct Bone Effects
While its primary role is mineral regulation, Vitamin D also has other direct and indirect effects on bone health. It plays a role in the function of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells), influencing the continuous remodeling process of bone. Additionally, Vitamin D supports muscle strength, which indirectly benefits bone health by reducing the risk of falls and subsequent fractures, especially in the elderly.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary and most vital role of Vitamin D in bone health is its ability to regulate and optimize the absorption and utilization of calcium and phosphorus. By ensuring these essential minerals are adequately absorbed from the diet and maintained at proper levels in the bloodstream, Vitamin D directly supports bone formation, mineralization, and strength. Maintaining sufficient Vitamin D levels through sun exposure, diet, or supplementation is therefore indispensable for preventing bone disorders and preserving skeletal integrity throughout life.