Optimize 3-day split for peak strength & lean mass gains?

Unlocking Potential: The Power of a 3-Day Split
For many aspiring lifters, balancing intense training with adequate recovery can be a challenging puzzle. The 3-day split, a popular and highly effective training methodology, offers a potent solution. By strategically dividing your training across three non-consecutive days, you can hit each major muscle group with sufficient frequency and intensity, allowing for optimal recovery and growth. This article will delve into how to fine-tune a 3-day split to achieve both peak strength and significant lean muscle gains.
Whether you’re a beginner looking for a solid foundation or an intermediate lifter aiming to break plateaus, a well-designed 3-day split can be your ticket to a more robust physique and improved performance. It allows for higher quality work per session compared to full-body routines, while also providing more recovery time than higher-frequency splits.

The Core Benefits of a Strategic 3-Day Split
Choosing a 3-day split comes with several inherent advantages that make it ideal for concurrent strength and hypertrophy goals:
- Adequate Recovery: With training days spread out (e.g., Monday, Wednesday, Friday), you get 24-48 hours rest between sessions, crucial for muscle repair and growth.
- High Training Intensity: Fewer training days per week mean you can pour more energy and focus into each session, leading to higher quality lifts and greater stimulus.
- Balanced Frequency: Each muscle group is typically hit once or twice per week depending on the split type, which is enough to stimulate growth without overtraining.
- Flexibility: Easily adaptable to busy schedules, making consistency more achievable.
Hitting Peak Strength: Key Strategies
To maximize strength within a 3-day split, your programming must prioritize compound movements and progressive overload. Strength training primarily operates in lower rep ranges with heavier weights.
- Compound Lifts First: Start your workouts with major compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, overhead presses, and rows. These movements engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, allowing you to lift the heaviest weights and generate the most strength stimulus.
- Progressive Overload: This is non-negotiable for strength. Consistently strive to increase the weight lifted, reps performed, or sets completed over time. Small, consistent increases add up significantly.
- Lower Rep Ranges: For your primary strength movements, aim for 3-6 repetitions per set. This range is optimal for developing maximal strength.
- Adequate Rest Between Sets: To recover central nervous system function and allow for maximal effort on subsequent sets, rest 2-5 minutes between heavy sets.
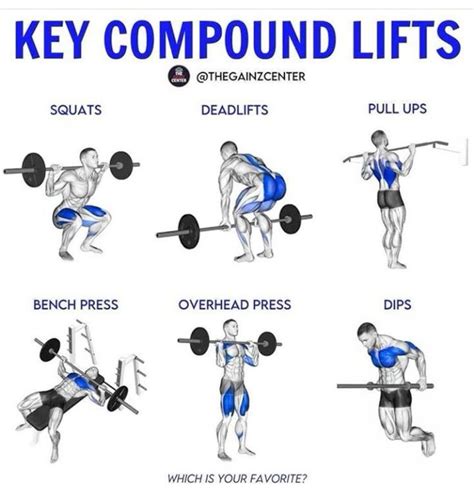
Sculpting Lean Mass: Hypertrophy Principles
While strength training will contribute to muscle mass, dedicated hypertrophy work targets muscle growth more directly. This involves higher volume and specific rep ranges.
- Volume and Time Under Tension: Increase the total number of sets and reps for each muscle group. For hypertrophy, aim for 8-12 repetitions per set for most exercises, focusing on a controlled tempo to maximize time under tension.
- Mind-Muscle Connection: Actively focus on contracting the target muscle during each repetition. This enhances muscle activation and helps recruit more muscle fibers.
- Accessory Exercises: Incorporate isolation exercises (e.g., bicep curls, tricep extensions, lateral raises) after your main compound lifts. These allow you to target specific muscles and further accumulate volume.
- Vary Rep Ranges: While 8-12 reps is standard, occasionally cycling through higher (12-15 reps) or even lower (6-8 reps) hypertrophy-focused ranges can provide varied stimulus for growth.
- Shorter Rest Periods: For hypertrophy-focused sets, rest 60-90 seconds between sets to maintain metabolic stress, which is a key driver of muscle growth.

Sample 3-Day Split: Push/Pull/Legs (PPL) for Strength & Mass
A Push/Pull/Legs (PPL) split is arguably the most popular and effective 3-day structure for concurrent strength and mass gains. Here’s a general template:
- Day 1: Push (Chest, Shoulders, Triceps)
- Strength Focus: Barbell Bench Press, Overhead Press
- Hypertrophy Focus: Incline Dumbbell Press, Lateral Raises, Triceps Extensions, Cable Flyes
- Day 2: Pull (Back, Biceps)
- Strength Focus: Barbell Rows, Pull-ups/Lat Pulldowns (weighted if possible)
- Hypertrophy Focus: Face Pulls, Dumbbell Rows, Bicep Curls, Shrugs
- Day 3: Legs (Quads, Hamstrings, Glutes, Calves)
- Strength Focus: Barbell Squats, Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs)
- Hypertrophy Focus: Leg Press, Hamstring Curls, Leg Extensions, Calf Raises
Remember to adjust exercises, sets, and reps based on your individual needs and recovery capacity. You can also alternate the order of exercises or specific movements each week to provide varied stimulus.

Beyond the Gym: Nutrition and Recovery
Your efforts in the gym will be wasted without proper support outside of it. Nutrition and recovery are equally critical for optimizing your 3-day split.
- Protein Intake: Aim for 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily to support muscle repair and growth.
- Caloric Intake: To build muscle, you generally need to be in a slight caloric surplus. For strength, maintaining a surplus or maintenance calories is often best.
- Carbohydrates and Fats: Ensure adequate intake of complex carbohydrates for energy and healthy fats for hormonal function.
- Sleep: Target 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. This is when the majority of muscle repair and growth occurs.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support performance and recovery.
- Deload Weeks: Periodically incorporate deload weeks (reduced intensity/volume) every 6-10 weeks to prevent overtraining and allow your body to fully recover and supercompensate.
Conclusion: Consistency and Adaptation are Key
Optimizing a 3-day split for peak strength and lean mass gains is an ongoing journey that requires consistency, smart programming, and attention to your body’s signals. By focusing on heavy compound lifts with progressive overload for strength, and incorporating higher volume accessory work with controlled tempos for hypertrophy, you create a powerful synergy. Combine this with diligent nutrition and adequate recovery, and you’ll be well on your way to building the robust, muscular physique you desire. Listen to your body, track your progress, and be prepared to adapt your routine as you get stronger and leaner.









