What are the primary advantages and disadvantages of using a helical gear over a spur gear in a high-speed, high-load application?

Introduction: Gear Selection in Demanding Applications
In the realm of mechanical engineering, selecting the appropriate gear type is paramount, especially for systems operating under high-speed and high-load conditions. The choice between a helical gear and a spur gear profoundly impacts performance, noise levels, efficiency, and system complexity. While both gear types are fundamental to power transmission, their distinct tooth geometries lead to significant differences in their operational characteristics. This article delves into the primary advantages and disadvantages of opting for a helical gear over a spur gear when designing for such challenging environments.
Understanding Spur vs. Helical Gears
Before examining their performance in demanding applications, it’s essential to understand the basic construction of each:
- Spur Gears: These are the simplest and most common type of gear. Their teeth are straight and run parallel to the axis of rotation. When two spur gears mesh, the contact occurs along the entire width of the tooth simultaneously.
- Helical Gears: In contrast, helical gears have teeth that are cut at an angle (known as the helix angle) to the gear’s axis of rotation. When meshing, the contact begins gradually at one end of the tooth and progresses across the tooth face, resulting in a more continuous engagement.
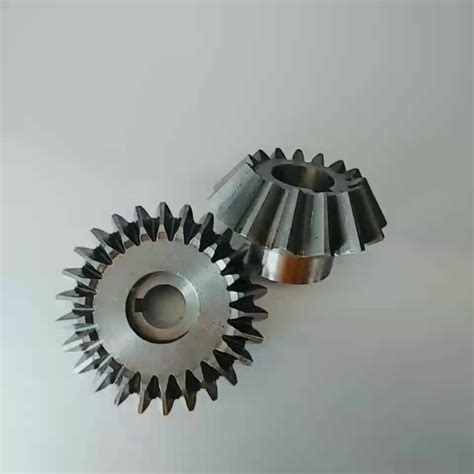

Primary Advantages of Helical Gears
For applications characterized by high speeds and significant loads, helical gears present several compelling advantages:
1. Smoother and Quieter Operation
One of the most significant benefits of helical gears, especially at high speeds, is their ability to operate much more smoothly and quietly than spur gears. The gradual, progressive engagement of helical teeth reduces the impact loading that occurs when spur gear teeth abruptly come into full contact. This continuous engagement minimizes vibrations and noise, making them ideal for applications where acoustic performance is critical or where high RPMs would make spur gears excessively noisy.
2. Higher Load Carrying Capacity
Helical gears typically boast a higher load-carrying capacity for a given face width compared to spur gears. This is due to the larger contact ratio and the fact that the load is distributed over a greater length of the tooth face, often with multiple teeth in contact simultaneously. This distributed load reduces stress concentrations on individual teeth, allowing them to transmit more power and torque without premature wear or failure.
3. Increased Contact Ratio
The angled teeth of helical gears result in an increased contact ratio, meaning that more teeth are typically in mesh at any given time. This continuous contact provides a smoother transfer of power, reduces the risk of tooth breakage under shock loads, and contributes to the overall robustness of the gear set in demanding conditions.
4. Suitable for High Speeds
The inherent smoothness and reduced vibration of helical gears make them exceptionally well-suited for high-speed applications. Unlike spur gears, where the sudden impact of teeth engagement can lead to dynamic loads and operational issues at high RPMs, helical gears maintain stable performance, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of the gear system.

Primary Disadvantages of Helical Gears
Despite their advantages, helical gears come with certain drawbacks that must be carefully considered, particularly in the context of high-speed, high-load applications:
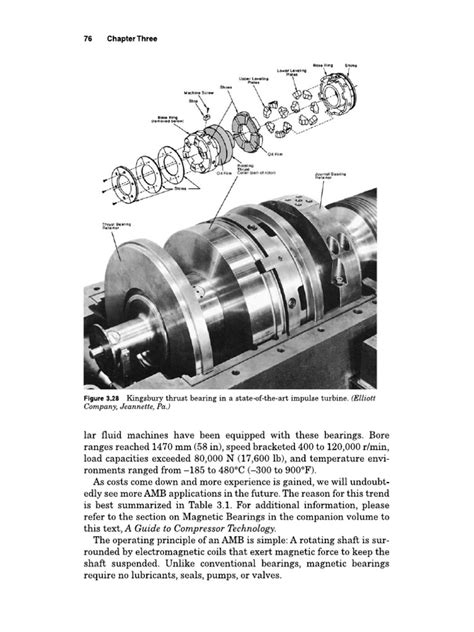
1. Axial Thrust Load
The most significant disadvantage of helical gears is the generation of an axial thrust force. Because the teeth are angled, the meshing action not only creates a tangential force (which transmits torque) but also an axial component that pushes the gears along their shafts. This axial thrust must be accommodated by robust thrust bearings, which adds complexity, size, and cost to the overall system design. In high-load applications, this thrust force can be considerable, requiring specialized bearing arrangements.
2. Increased Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Producing helical gears is inherently more complex and costly than manufacturing spur gears. The process of cutting angled teeth requires more sophisticated machinery and precise control, leading to higher production expenses. This cost factor can be a significant consideration, especially for mass production or when budget constraints are tight.
3. Potential for Higher Friction and Heat Generation
While the initial engagement of helical teeth is smoother, the sliding action along the helix angle can lead to more friction and potentially higher heat generation compared to the more purely rolling contact of spur gears. In high-speed, high-load applications, this increased heat can affect lubrication effectiveness and potentially reduce efficiency, necessitating more advanced cooling or lubrication systems to manage thermal loads.
Conclusion: Balancing Performance and Practicality
For high-speed, high-load applications, helical gears often emerge as the superior choice due to their inherent advantages in smooth, quiet operation, and enhanced load-carrying capacity. They minimize vibration and noise, crucial for dynamic systems, and can handle greater stresses without compromise. However, these benefits do not come without trade-offs.
The generation of axial thrust necessitates the integration of specialized thrust bearings, adding complexity and cost to the design. Furthermore, the manufacturing process for helical gears is more intricate and expensive, and the potential for increased friction and heat generation requires careful consideration of lubrication and thermal management. Ultimately, the decision to use helical gears over spur gears in a high-speed, high-load scenario involves a detailed engineering analysis, balancing the need for superior performance against the practical implications of increased system complexity and cost.